Mission Divyastra
India successfully tests Agni-5 missile with MIRV technology, named ‘Mission Divyastra’ from Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island in Odisha.
- Trial conducted by – DRDO
- Mission – It is the 1st flight test of indigenously developed Agni-5 missile with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology.
- The system is also equipped with indigenous avionics systems and high accuracy sensor packages along with MIRV technology.
Agni missiles are the main land-based delivery systems for India’s nuclear weapons. Agni-5, a long range (6000km) ballistic missile, uses a 3-stage solid fuelled engine. All the Agni series missiles inducted can now carry only a single warhead.
- MIRV – A single missile carrying several nuclear warheads, each to be released at different speeds with different trajectories to hit different targets hundreds of kilometers apart.
MIRV was developed in the Cold War with US testing it at first in 1970s. At present, USA, Russia, UK, and France have MIRV missiles. Pakistan is also developing such missiles.
|
MIRV Missiles
|
|
Land variant
|
Submarine variant
|
Both land and submarine variant
|
|
China
|
USA, the UK and France
|
Russia
|
- Number of warheads – It depends on its design, weight, size, range and other parameters.
- India’s Agni-5 test flight can carry 3 to 4 warheads, while there are other systems that can carry as many as 15 warheads, or even more.
- Challenges - Development requires the combination of large missiles, small warheads, accurate guidance, and a complex mechanism for releasing warheads sequentially during flight.
- Advantages of MIRV – One missile can inflict multiple damages thus also cost effective.
- It also has the ability to penetrate missile defence systems and can be made to carry decoy warheads to confuse the defence system.
- Significance – A significant boost to credible strategic deterrence against China and also strengthens India’s claim for a place in future arms control negotiations.
- The project director was a woman and there were significant contributions from other women scientists.
- India’s Nuclear Triad
- Land vector – Prithivi-II, Agni-1, Agni-2, Agni-3, Agni-5.
- Air Vector – Sukhoi-30MKI, Mirage-2000, Jaguar & Rafale fighter jets.
- Sea vector – Only INS Arihant, nuclear powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN).
References
- Deccan Herald| Successful trial of Mission Divyastra
- Times of India| Nuclear Triad
Trends in International Arms Transfers, 2023 Report
According to a new report ‘Trends in International Arms Transfer 2023, India continues to be the world’s top arms importer.
- Published by – Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI).
- Study period – 2019-2023
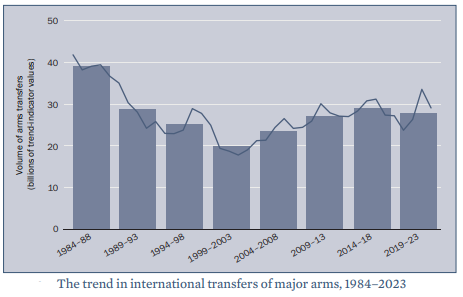
- Export regime – The 5 largest exporters were the United States, France, Russia, China and Germany.
- For the 1st time, France became the 2nd biggest arms exporter after the USA.
- The USA and Western Europe together accounted for 72% of all arms exports in 2019-2023.
- Imports – The 5 largest arms importers were India, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Ukraine and Pakistan.
- States in Asia and Oceania accounted for 37% of all arms imports, followed by states in the Middle East, Europe, the Americas and Africa.
- For the 1st time in 25 years, the US has become the largest supplier to Asia and Oceania.
- Pakistan is 5th largest arms importer in 2019-23 where China provides 82% of arms imports.
- India – Its arms imports increased by 4.7% between 2014–2018 and 2019–2023.
- Russia is India’s main-arms-supplier, accounting for 36 % of its arms imports.
The period between 2014 and 2018 was the 1st 5-year stretch in 50 years (since 1960-1964) when deliveries from Russia or the erstwhile Soviet Union (prior to 1991) made up less than half of India’s arms imports.
- India & France – India was the largest single recipient of French arms exports, accounting for nearly 30%.
- The Indian Air Force operates 36 Rafale fighter jets customised in accordance to its needs.
- Furthermore, India is in talks for 26 Rafale Marine jets to be procured for the Navy’s aircraft carrier INS Vikrant from France.
|
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute
|
- An independent international institute dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament.
- Established in – 1966, in Stockholm, Sweden
- Role – It provides data, analysis and recommendations, based on open sources, to policymakers, researchers, media and the interested public.
- Vision – A world in which sources of insecurity are identified and understood, conflicts are prevented or resolved, and peace is sustained.
- Mission – To undertake research, activities on security, conflict and peace and provide recommendations to facilitate dialogue and build capacities.
- To promote transparency and accountability and to deliver authoritative information to global audiences.
|
References
- The Print| India is the world’s largest arms importer globally
- SIPRI| Trends in International Arms Transfer, 2023
CAROTAR
Thailand objected to India’s custom regulation, CAROTAR at the ongoing India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement (FTA) review.
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a grouping of 10 Southeast Asian states which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic integration amongst its members.
- CAROTAR – Customs (Administration of Rules of Origin under Trade Agreements) Rules.
- Nodal agency – Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs.
- Implemented in – 2020.
- Aim – To regulate domestic importers by strictly verifying the rules of origin under the free trade agreements (FTAs) and to curb the influx of Chinese products claiming fraudulent exemptions under the guise of ASEAN exports.
- Need – Earlier, merely a country of origin certificate, issued by a notified agency in the country of export was sufficient to avail the benefits of FTAs.
- It was exploited in many cases to avail duty concessions.
- Provisions – It mandates the supplier to provide the Indian purchaser with a Certificate of Origin (CoO) from the issuing authority in the exporter’s state, confirming the product’s origin for import validation.
- Imported products should have undergone value addition of at least 35% in the countries of origin.
- Keep the origin related information specific to every Bill of Entry (B/E) for a minimum of 5 years.
- Significance – It prevents a country that has FTA with India from dumping goods from some 3rd country in the Indian market by just putting a label on it.
- Concerns – India-ASEAN trade gap in FY23 surged to $43.57 billion in favour of bloc countries as several multinational companies are increasing investments in ASEAN nations as part of their China-plus-one policy.
- India’s production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes have also increased demand for intermediate products that are being sourced from ASEAN countries.
The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) is a trade deal between ASEAN and India, which came into effect in 2010 to steadily increasing trade between ASEAN and India.
Reference
The Indian Express| Thailand objects to India’s CAROTAR
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain 2024 Campaign
Recently, the 5th edition of the ‘Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain’ campaign was launched.
- A transformative movement towards a water-secure and sustainable future.
Jal Shakti Abhiyan, launched by the Ministry of Jal Shakti in 2019 as a “Jan Andolan”, to initiate water conservation at the grass-root level through citizen participation across the country.
- Started in – 2021, as part of Jal Sanchay and has become an annual feature.
- Nodal agency – National Water Mission, Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation in collaboration with Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation.
- Aim – To nudge states and other stakeholders to create rain water harvesting structures suitable to the climatic conditions and sub-soil strata before the monsoon.
- Coverage – All the blocks of all districts (rural as well as urban areas) across the country.
- Focused interventions
- Water conservation and rainwater harvesting.
- Enumerating, geo-tagging & making inventory of all water bodies and preparing scientific plans for water conservation.
- Setting up of Jal Shakti Kendras in all districts
- Intensive afforestation
- Awareness generation.
- JSA: CTR 2024 – It will have a distinctive emphasis on
- De-silting and cleaning of water bodies.
- Revitalizing Abandoned/Defunct Borewells for groundwater recharge and Rejuvenation of Small Rivers.
- Geo-tagging of water bodies, coupled with meticulous mapping and regular updates in the State's revenue records
- Intensified afforestation efforts in the catchment areas of water bodies.
- Snow harvesting in hilly areas like stupas in Ladakh.
- Implemented period – March to November, 2024, the pre-monsoon and monsoon period in the country.
- 2024 Theme – ‘Nari Shakti se Jal Shakti’, to recognise and appreciate the crucial role played by women in water management, conservation and sustainability.
- It will establish a powerful connection between the ‘Nari Shakti’ and the sustainable management of water resources i.e. Jal Shakti.
Approximately 24 lakh women have been trained for testing water samples using Field Testing Kit (FTK) to ensure quality of piped water supply.
Reference
PIB| India launches JSA: Catch the Rain Campaign 2024
Living Animal Species (Reporting and Registration) Rules, 2024
The Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change has notified the Living Animal Species Rules 2024.
- CITES – It is an international agreement between government’s aims to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten the survival of the species.
- India is a party to the CITES, which requires that appropriate measures are taken to enforce the provisions of the Convention.
- Need – Voluntary Disclosure Scheme (VDS) in 2020 created the opportunity to launder illegal stocks of exotic CITES species.
According to recent reports, more than 70,000 native and exotic species were trafficked via air.
- Rules – All persons possessing a living specimen of an animal species shall apply for registrations within a period of 6 months from the date of commencement of these rules.
- And thereafter within 30 days of possession of such animal species, report to the concerned State Chief Wild Life Warden, through the PARIVESH 2.0 portal
- Further, any transfer of possession and birth of offsprings of such specimen(s) shall also be registered and death of such specimen(s) shall be reported.
- Animal species – Any living specimens of any animal species listed in Schedule IV appended to the 1972 Wildlife Protection Act which covers species under CITES.
- It does not apply to other wildlife that is already protected under the Wildlife Protection Act and cannot be kept in captivity
Quick Facts
- Section 49 M of the Wildlife (Protection) Amendment Act 2022 - It provides for registration of possession, transfer, reporting of birth and death of living scheduled animal species which are listed in the Appendices of CITES and listed in the Schedule IV of the Act.
- Appendix 1 of schedule 4 – It includes endangered exotic animals and plants and import rules are stricter for them.
- Section M of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 – It mandates that anyone possessing exotic wild animals listed under Schedule IV of the Act must obtain a registration certificate from the Management Authority to comply with CITES regulations.
- Breeders of Species Licence Rules, 2023 – Those who breed exotic species protected under CITES and listed in Appendix 1 of schedule IV of Wildlife Protection Act 2022 can now obtain Breeders of Species Licence.
Reference
Hindustan Times| Mandate registration of Animal Species
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme
|
|
Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers announces the Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance (RPTUAS) Scheme recently.
- The revamped Pharmaceutical Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (PTUAS) extends the scheme's scope to include any pharmaceutical manufacturing unit with a turnover of less than Rs. 500 crore.
- It entails financial assistance to drug companies to help them upgrade their facilities to produce medicines conforming to Revised Schedule-M & WHO-GMP standards.
- It also introduces more flexible financing options, emphasising subsidies on reimbursement basis, over traditional credit-linked approach.
- Pharmaceutical Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (PTUAS)
- It is a credit-linked scheme aims to help small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) meet national and international regulatory standards.
|
India is a major exporter of medicines to low/middle-income countries (LMICs) which require WHO GMP certification.
|
|
|
Dilli Gramodaya Abhiyan
|
|
Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation inaugurated commencement of PNG facilities in under the ‘Dilli Gramodaya Abhiyan’ recently.
- Dilli Gramodaya Abhiyan aims to develop and create necessary infrastructure in the urbanized villages and new urban areas of Delhi.
- It is executed by the Delhi Development Authority (DDA).
|
|
National Speed Breeding Crop Facility
|
|
Union Minister of Science & Technology inaugurated the National Speed Breeding Crop Facility in Punjab.
- It is the India’s 1st Speed Breeding Crop Facility opened at the National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) in Mohali, Punjab.
- It will augment transformational changes in crop improvement programme by accelerating the development of advanced crop varieties with implementation of speed breeding cropping methods.
- National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) is the first Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute, established in India in 2010.
- NABI aims at catalyzing the transformation of Agri-food sector.
- NABI has contributed to ‘Atal Jai Anusandhan Biotech (UNaTI) Mission (Poshan Abhiyan), and Biotech Kisan Hubs for Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana etc.
|
|
KIRTI Programme
|
|
Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports to inaugurate Khelo India Rising Talent Identification (KIRTI) programme.
- It aims to create a pyramidal structure starting from the grassroots level and culminating in the development of elite athletes for achieving excellence at international platforms.
- KIRTI aims to conduct 20 lakh assessments across the country throughout the year to identify talent through notified Talent Assessment Centres.
- The Target Olympic Podium Scheme sits at the top of the pyramid.
- Targeted age-group -9 to 18 years i.e. school-going age.
- It is a nation-wide programme under the Khelo India mission (To revive the sports culture in India at the grass-root level).
Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS)
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports (MYAS) launch it in 2014.
- It is an attempt to assist India’s top athletes and revamped in 2018 to establish a technical support team for managing the TOPS athletes and providing holistic support.
Khelo India Scheme
- The Khelo India Scheme is the flagship Central Sector Scheme of the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports.
- Khelo India Mission aims at infusing sports culture and achieving sporting excellence in the country thus allowing the populace to harness the power of sports through its cross-cutting influence.
|
|
INSAT-3DS
|
|
INSAT-3DS, has initiated Earth imaging operations capturing the first set of images recently.
- INSAT-3DS is a meteorological satellite launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in February 2024.
|
Satellite
|
Salient features
|
|
Mission
|
Meteorological services, Data relay and Satellite Aided Search & Rescue services.
|
|
Payloads
|
6-channel Imager and a 19-channel Sounder.
|
|
Orbit
|
Geostationary orbit
|
|
Launch Vehicle
|
GSLV
|
- The mission is fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- It is designed for enhanced meteorological observations and monitoring of land and ocean surfaces for weather forecasting and disaster warning.
- The satellite will augment the Meteorological services along with the presently operational INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR satellites.
|
|
Vajra Sentinel System
|
|
Big Bang Boom Solutions Private Limited (BBBS) secured an order from the IAF and Indian Army under the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) initiative.
- The Vajra Sentinel System is an anti-drone system that can detect, track, and neutralize drones at extraordinary ranges.
- It is designed by Big Bang Boom Solutions Private Limited (BBBS), Chennai based defense startup.
- This is the largest contract signed by the MoD under the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) initiative.
- The system’s core sensor, built around Artificial Intelligence and computer vision algorithms, enables precise identification, classification and location identification of drones.
- It utilises passive RF sensor technology to eliminate false alarms, and its sensor and jammer combination meets stringent military standard specifications for durability and reliability.
- It has a number of state-of-the-art tech improvements such as Advanced Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar and kamikaze drones which can be upgraded on demand by the user.
- The system’s core sensor, built around Artificial Intelligence and computer vision algorithms, enables precise identification, classification and location identification of drones.
|
|
Democracy Report 2024
|
|
India was downgraded on multiple metrics to emerge as one of the worst autocratisers according to the Democracy Report 2024.
- It is an annual democracy report released by the Gothenburg-based V-Dem Institute.
- The report categorizes countries into 4 regime types based on their score in the Liberal Democratic Index (LDI)
- Liberal Democracy
- Electoral Democracy
- Electoral Autocracy
- Closed Autocracy
- The report maps each country on a matrix of whether they are turning more democratic (democratising) or more autocratic (autocratising).
Findings
- According to the report in 2023, 71% of the world’s population live in autocracies, 42 countries (home to 35% of the world’s population) were undergoing autocratisation.
- India (18% of the world’s population) accounts for about half of the population living in autocratising countries.
- Democratisation was taking place only in 18 countries, accounting for just 5% of the world’s population.
India was downgraded to the status of an electoral autocracy in 2018.
|
|
Pi (Personal intelligence)
|
- Pi is the 1stemotionally intelligent AI chatbot with which one can have deep and meaningful conversations.
- It is launched by Inflection AI, a California-based AI startup founded by former co-founders of DeepMind and LinkedIn.
- It is designed to understand natural language, generate relevant, engaging responses, and handle a wide range of topics.
|
|
Miscophus Kaleshi
|
|
Zoological Survey of India discovers new species of Digger Wasp.
- The new digger wasp species named as Miscophus Kaleshi in honour of researcher and Doctor Kalesh S. in Thiruvananthapuram.
- It is one of the 2 new wasp species discovered in south India’s habitats.

|
|
Selection rules for district judges
|
- The Supreme Court said that states could not consult Union government on the selection and appointment of judicial officers.
- The SC verdict said:
- Any issue between High Court (HC) and state government should have been ironed out in the course of the consultative process within the two entities.
- The state government was bound to consult only the High Court.
- Any other exercise de hors such consultation would not be in accordance with the scheme of the Constitution.
|
