The 12th meeting of Interpol’s Match-Fixing Task Force (IMFTF) concluded with a call for harmonised global efforts to curb competition manipulation and establishment of national platforms, as outlined by Macolin Convention.
It was the first major event held under the banner of its newly created Financial Crime and Anti-Corruption Centre (IFCACC).
Reference
Retail Inflation had grown by 7.8% in April, 2022. This is at its highest in the last 8 years, and almost twice the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI's) target.
|
Category of the CPI |
Weightage |
|
Food Items |
46% of the index |
|
Fuel & Light |
7% of the index |
|
Core Inflation (All other items) |
47% of the index |
The way out is for the RBI to raise interest rates in a credible fashion. The difficulty is that raising interest rates at the current juncture, when growth is iffy, could lead to concerns of stagflation.
Reference
|
REITs |
InvITs |
|
REITs comprise a portfolio of commercial real estates; a major portion is already leased out. |
InvITs comprise a portfolio of infrastructure assets such as highways and power transmission assets. |
|
REITs are investment vehicles that own and manage investment grade and income-producing real estate properties (such as offices, malls, industrial parks, hospitality, etc.) |
InvITs are investment vehicles that invest in infrastructure projects (such as roads or highways). |
|
REITs must be publicly listed. |
InvITs can be publicy listed, private listed or private unlisted. |
|
REITs provide stable income and yield as 80% of REIT assets are income-generating assets with long-term rental contracts. |
InvITs’ cash flows are less certain as they are dependent on multiple factors, including the capacity utilisation of the underlying assets and scalability of tariffs. |
|
REITs are more accessible to small investors and have higher liquidity due to lower unit prices and trading lots. |
InvITs have a bigger trading lot size and thus somewhat poor liquidity. |
|
REITs own the property leased out and their underlying assets see growth in value over time and have high terminal value.
REITs have greater visibility of growth, which can be achieved by redeveloping existing assets, new construction, and acquiring completed leased assets. |
For InvITs, growth depends on the successful acquisition of concession assets through a bidding process.
InvITs comprise concessions where the projects are returned to the authority or rebid post the concession period. |
Reference
Under normal conditions, the RNA granules are present in the cytoplasm at low numbers.
But, they increase in number and size under stressful conditions including diseases.
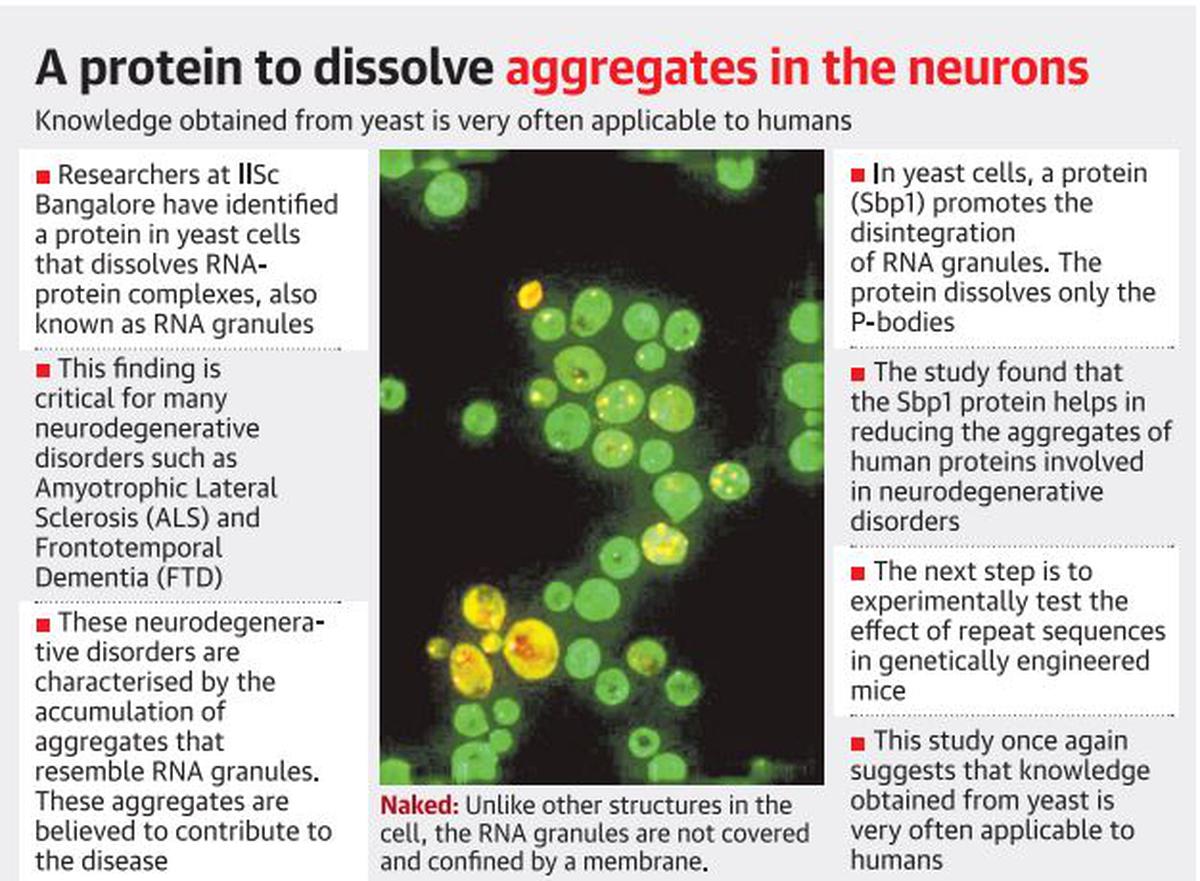
Reference