As part of One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) Initiative, India, Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Singapore are in advanced stages of creating a mega grid infrastructure.
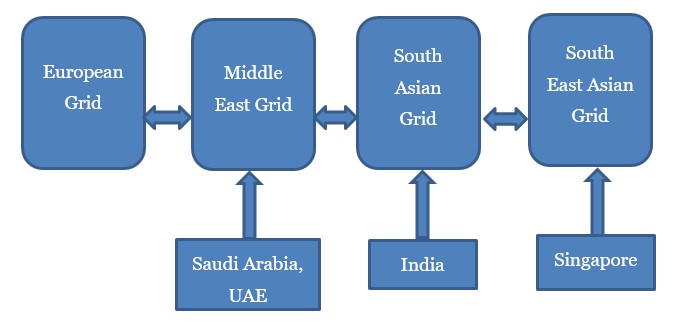
One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG
References
The Centre launched the Unified Portal for Agricultural Statistics (UPAg) to address the complex governance challenges India’s farm sector is facing now.
References
Researchers at the University of Princeton have developed a String technique that can drastically reduce the amount of land and time needed for production.
According to McKinsey report, the total demand for lithium is expected to grow to between 2 to 3 million tons by 2030.
String Technique
References
Indian Express | String Technology for Lithium production
Odisha is reeling from two major disease outbreak, Scrub Typhus and Leptospirosis which have killed six people in the state so far.
Scrub Typhus
Leptospirosis
References