Unmanned Aerial Systems (Drone) Common Testing Centre
India’s first Unmanned Aerial Systems Common Testing Centre to be established in Tamil Nadu.
- UAS are air vehicles and associated equipment that do not carry a human operator, but instead are remotely piloted or fly autonomously.
- Location – The UAS Common Testing Centre would be established at the SIPCOT Industrial Park, Vallam Vadagal near Sriperumbudur.
- It will be established under Defence Testing Infrastructure Scheme (DTIS).
- Aim – To enable the State a significant contributor to the self-reliance of the country in the aerospace and defence sectors.
- Tamil Nadu Industrial Development Corporation (TIDCO) is the nodal agency for the implementation of the Tamil Nadu Defence Industrial Corridor (TNDIC).
- As part of the implementation of the TNDIC, the government is about to create an enabling ecosystem including Common Testing Centres for the Aerospace and Defence Industry.
An integrated facility for testing for UAS (Drone) is available only with DRDO at Chitradurga, Karnataka.
Defence Testing Infrastructure Scheme (DTIS)
- Aim - To boost domestic defence & aerospace manufacturing.
- Launch - May 2020.
- Ministry - Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- Duration - 5 years.
- It envisages setting up of 6-8 greenfield defence testing infrastructure facilities that are required for defence and aerospace related production.
- Funding Pattern - 75% Government funding in the form of ‘Grant-in-Aid’ + 25% to be borne by the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) constituents.
References
1. The Hindu | Unmanned Aerial Systems (Drone) Common Testing Centre
2. Business Standard | India's first drone common testing centre
3. The Hindu Businessline | India’s first drone common testing centre
4. PIB | Defence Testing Infrastructure Scheme
PM Vishwakarma
Union Cabinet has recently approved a new Central Sector Scheme ‘PM Vishwakarma’.
- Aim - To support traditional artisans and craftspeople (Vishwakarmas) of rural and urban India.
- It will be launched on the forthcoming Vishwakarma Jayanti (17 Sept, 2023).
- Duration - 5 years (FY 2023-24 to FY 2027-28).
- Ministry - Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises.
- Significance – It aims at improving the quality, as well as the reach of products and services of Vishwakarmas and to ensure that they are integrated with the domestic and global value chains.
- 18 traditional trades will be covered in the first instance under PM Vishwakarma.
- Benefits - Under this scheme, Vishwakarmas will be provided recognition through
- PM Vishwakarma certificate and ID card,
- Credit Support upto Rs.1 lakh (First Tranche) and
- Rs.2 lakh (Second Tranche) with a concessional interest rate of 5%.
- The scheme will further provide skill upgradation, toolkit incentive, incentive for digital transactions and marketing support.
- Participants will get a stipend of Rs.500 per day while undergoing training.
- Beneficiaries will also receive up to Rs. 15,000 to buy modern tools.

References
1. PIB | PM Vishwakarma
2. Economic Times | Vishwakarma scheme
3. Hindustan Times | PM Vishwakarma Scheme
PM-eBus Sewa
The Cabinet has recently approved a bus scheme “PM-eBus Sewa”.
- The scheme is about introducing around 10,000 electric buses under the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model in 169 cities across the nation.
- The scheme will promote e-mobility and provide full support for behind-the-meter power infrastructure.
- The scheme was first announced in 2021 in the Union budget.
- Coverage - The scheme will cover cities having a population of 3 lakh and above according to Census 2011.
- Under this scheme priority will be given to cities having no organized bus service.
- Duration - The Scheme will support bus operations for 10 years.
- Ministry - Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs.
- The Scheme has 2 segments
- Segment A – Augmenting the City bus services - (169 cities)
- Segment B – Green Urban Mobility Initiatives (GUMI) - (181 cities).
- Funding - Estimated cost of the scheme is Rs 57,613 crore, of which Rs 20,000 crore will be provided by Central government and the rest will be provided by state governments.
- Operation - States/Cities shall be responsible for running the bus services and making payments to the bus operators.
- This scheme is different than the one that is rolled out by the Convergence Energy Services Ltd (CESL).
CESL is a wholly owned subsidiary of Energy Efficiency Services Limited, under the Ministry of Power.
References
1. PIB | PM-eBus Sewa
2. The Hindu Businessline | PM-eBus Sewa
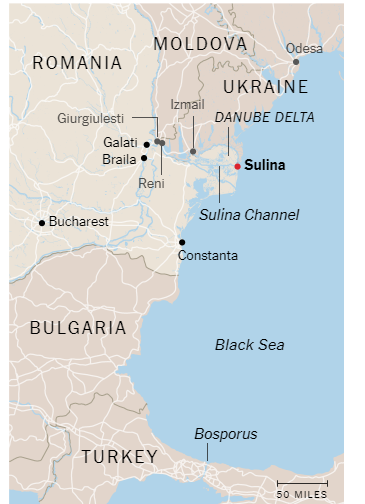
Sulina Channel
The Sulina Channel is the new alternative trade route after Russia’s drone strikes on ports and grain storage facilities along the Danube river in Ukraine.
- Danube River - Danube is the Europe’s second longest river which has been historically crucial for the movement of freight.
- It starts at the intersection of two smaller rivers in Southwestern Germany - Brigach and Brech Rivers.
- It passes through countries including Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Germany, Hungary, Moldova, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Ukraine.
- Before Russia pulled out of the safe passage corridor, the Danube ports accounted for around a quarter of Ukraine's grain exports.
- Recently, Russia attacked the inland Danube ports of Reni and Izmail.
- Channels - Chilia, Sulina and St George.
- Sulina Channel - It is situated in Romania (a NATO member).
- It is the only one deep and wide enough channel fits for freight transport among the three channels.
- Ships carry grain from Ukraine leave from Ukrainian ports such as Izmail and Reni on the mainstream (or the Chilia Channel), and head to the port of Sulina.
- Grains are shipped downriver through territorial waters of European Union and Romania, and onwards from Romania's Black Sea port of Constanta.
- It is a sort of a riverine ‘expressway’ crucial for transport of goods from Ukraine (one of the world's top grain exporters) to the Black Sea.
- This route is under constant surveillance and protection of NATO.
- Challenges
- Limited holding capacity
- Sheer traffic
Reference
The Indian Express | Sulina Channel
Incremental CRR (ICRR)
RBI has announced that it will be imposing an incremental cash reserve ratio (ICRR) of 10% on the increase in banks net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) between May 19 and July 28.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) - Banks are mandated to maintain a certain proportion of their deposits and specific liabilities as liquid cash with the RBI, which is called as cash reserve ratio.
- This is a tool at the disposal of the RBI to control the liquidity in the economy and can also act as a buffer in periods of bank stress.
- Banks are previously required to maintain 4.5% of their Net Demand and Time Liabilities as CRR with the RBI.
- RBI has the option to impose incremental credit reserve ratio, in addition to the CRR, in periods of excess liquidity in the system.
- RBI’s recent move – Effective from August 12, 2023, all scheduled banks must uphold an additional cash reserve ratio equating to 10% of the surge in their net demand and time liabilities (NDTL) recorded between May 19, 2023, and July 28, 2023.
- It will apply to all scheduled banks, including commercial banks, cooperative banks, and regional rural banks.
- It is a temporary measure which will be reviewed in 3 months.
- Reason – ICRR is a temporary measure to drain excess liquidity from the banking system due to its withdrawal of Rs 2,000 notes.
- Impacts - As liquidity is withdrawn, banks will have limited funds for lending, thereby decreasing demand for goods and services.
- This will consequently reduce the prices.
- Short-term interest rates might rise due to tightening of fund supply in the economy, acting as an additional measure to counter inflation.
- It may tie up bank resources and exert upward pressure on market rates.
References
1. The Hindu Businessline | Incremental CRR
2. The Hindu Businessline | ICRR

