Tardigrade

Beresheet

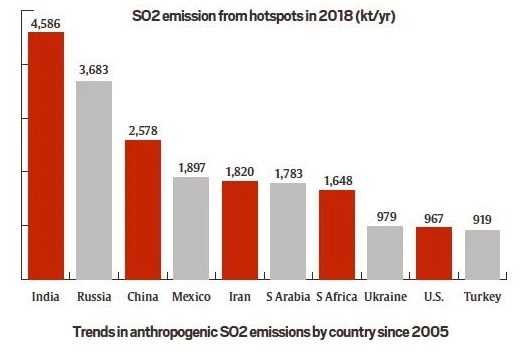
Sulphur dioxide emission
Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) - a timely policy intervention
Source: PIB, The Indian Express

Arhakarapprvvha 5 years
Sulfur dioxide is a gas. It is invisible and has a nasty, sharp smell. It reacts easily with other substances to form harmful compounds, such as sulfuric acid, sulfurous acid and sulfate particles.
About 99% of the sulfur dioxide in air comes from human sources. The main source of sulfur dioxide in the air is industrial activity that processes materials that contain sulfur.
eg the generation of electricity from coal, oil or gas that contains sulfur. Some mineral ores also contain sulfur, and sulfur dioxide is released when they are processed. In addition, industrial activities that burn fossil fuels containing sulfur can be important sources of sulfur dioxide.
Sulfur dioxide is also present in motor vehicle emissions, as the result of fuel combustion. In the past, motor vehicle exhaust was an important, but not the main, source of sulfur dioxide in air. However, this is no longer the case.
Sulfur dioxide affects human health when it is breathed in. It irritates the nose, throat, and airways to cause coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, or a tight feeling around the chest. The effects of sulfur dioxide are felt very quickly and most people would feel the worst symptoms in 10 or 15 minutes after breathing it in.
Those most at risk of developing problems if they are exposed to sulfur dioxide are people with asthma or similar conditions.
Because of the adverse health effects of high levels of sulfur dioxide, The following steps to manage and reduce the amount of sulfur dioxide produced. These include: