Few days ago, a Zero FIR was filed in connection with the Manipuri two Kuki-Zomi women incident.
FIR
The Apex court in Lalita Kumari v. Government of U.P. observed that it is mandatory to register a FIR under Section 154 if the complaint is related to a cognizable offence.
Zero FIR
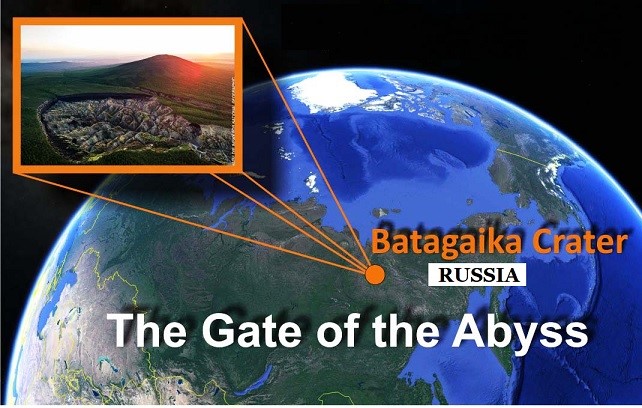
Drone footage has revealed details of Batagaika crater, a 1 kilometre long gash in Russia's Far East that forms the world's biggest permafrost crater.
Batagaika Crater
Russia is warming at least 2.5 times faster than the rest of the world.
Permafrost thawing
Union minister Jitendra Singh has said that Jammu is going to pioneer India's first cannabis medicine project undertaken by the CSIR-IIIM.
Cannabis
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) finds Chhattisgarh mining department underutilized DMFT, delayed projects.
The PMKKKY is a programme meant to provide for the welfare of areas and people affected by mining related operations, using the funds generated by District Mineral Foundations (DMFs).
The CAG report found several irregularities in the working of the trust, including the delays in projects and underutilisation of funds from the time the DMFT was first established in 2015 to March 2021.
Silver cockscomb which is widely regarded as a weed is found to have benefits that is being largely used by the Soliga tribal community.
Silver Cockscomb
Although it is of the same family as spinach, silver cockscomb leaves have lower levels of oxalic acid (0.2%) and phytic acid (0.12%). Spinach leaves on the other hand are high in calcium, oxalates, vitamin K and potassium, which can lead to formation of kidney stones.
Soliga tribe