Arogya Manthan 2023
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is organising Arogya Manthan to celebrate 5 years of Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana and 2 years of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission.
- Aim - To have insightful discussions and deliberations on challenges, trends, and best practices related to the two schemes.
- Hosted by - National Health Authority (NHA), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
- Both the flagship healthcare schemes aim to provide accessible, available, affordable and scalable healthcare to achieve the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in India.
Universal health coverage (UHC) means that all people have access to the full range of quality health services they need, when and where they need them, without financial hardship.
National Health Authority (NHA)
- It is the apex body responsible for implementing Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana.
- It has been entrusted with the role of designing strategy, building technological infrastructure and implementation of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission to create a National Digital Health Eco-system.
- National Health Authority is the successor of the National Health Agency.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)
- Launch – In 2018 as recommended by the National Health Policy 2017.
- Aim – It is a progression towards promotive, preventive, curative, palliative and rehabilitative aspects of Universal Healthcare.
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme having central sector component under Ayushman Bharat Mission.
- Ministry - Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
- It was launched to achieve the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- It consists of two components
- Health and wellness Centres and
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
- The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) was founded along with this scheme to make healthcare more convenient for citizens.
Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)
- Launched - 2021.
- Aim - To develop the backbone necessary to support the integrated digital health infrastructure of the country.
- It will bridge the existing gap amongst different stakeholders of Healthcare ecosystem through digital highways.
- The ABDM aims to provide Unique Digital Health IDs (UHID) for all Indian citizens to help hospitals, insurance firms, and citizens access health records electronically when required.
- National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare will be the implementing Agency.
Reference
- PIB | Arogya Manthan 2023
Five Eyes
Hardeep Nijjar killing: US envoy confirms Canada got ‘Five Eyes’ intelligence against India.
- Five Eyes refers to an intelligence-sharing alliance of the United States, United Kingdom, Australia, Canada and New Zealand.
- Origin - The alliance originated during the Second World War.
- In 1943, the Britain-USA (BRUSA) agreement laid the foundations for what became the UK-USA (UKUSA) agreement, signed in 1946.
- Canada joined it in 1949, and New Zealand and Australia did so in 1956, forming the alliance.
- Working - The Five Eyes members use communications methods, including signals intelligence (SIGINT), to monitor the citizens of other member countries.
SIGINT is intelligence derived from electronic signals and systems used by foreign targets, such as communications systems, radars, and weapons systems that provides a vital window for our nation into foreign adversaries' capabilities, actions, and intentions.
- In 2016, the Five Eyes Intelligence Oversight and Review Council came into being.
- Recent issue – The intelligence shared among Five Eyes partners had prompted Canadian Prime Minister’s allegations against India.
References
- The Indian Express | Five Eyes Alliance
- Hindustan Times | Hardeep Nijjar killing
- The Hindu | Canada intelligence on Nijjar’s killing
- The Times of India | Five Eyes
The Draft Patents (Amendment), Rules, 2023
The draft patent amendment rules were released recently.
- It is a further amendment to the Patents Rules, 2003 of the Patents Act, 1970.
- Released by - The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade for stakeholder.
Recent important Changes
- Fee - The rules have introduced a variable fee for filing pre-grant oppositions.
- The proposed introduction of fees can run into thousands of rupees, thus impose a financial burden on civil society organisations and patients’ groups filing pre-grant opposition.
- Pre-grant opposition is an important public health safeguard against patent ever greening and unmerited monopolies.
Patent ever greening refers to the continuing extension of patent rights, by obtaining many patents for the same item.
- Powers - The draft rules authorizes any person to file a pre-grant opposition but the maintainability of the petitioners will not be automatic and will be determined by the Controller.
- Time limit - The applicant is required to keep the Controller informed for the patent filed in any country apart from India, is reduced from 6 months to 2 months from the date of issuance.
- If the Controller sought information regarding any objection for novelty or patentability the same has to be furnished by the applicant within 6 months.
- An addition allows a patent applicant to file a divisional application regarding an invention disclosed in the provisional specification.
The Patents Rules, 2003
- They came into force on the date on which the Patents (Amendment) Act, 2002 comes into force.
- Features - No patent shall be granted before the expiry of a period of 6 months from the date of publication of the application.
- The Controller shall consider such representation only when a request for examination of the application has been filed.
The Patents Act, 1970
- This act is for patenting system in India came into force in the year 1972.
- It replaced the Indian Patents and Designs Act 1911.
Reference
The Hindu | Draft patent amendment rules 2023
Willful Defaulters
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) proposed that lenders should classify a borrower as a wilful defaulter within 6 months of their account being declared a non-performing asset (NPA).
- Wilful Defaulter - A willful defaulter is an entity or a person that has not paid the loan back despite the ability to repay it.
- A fraudster is one who intentionally cheats the bank with false documents/information and misappropriates the money.
- As per the RBI regulations, willful default covers several broad areas:
- Deliberate non-payment of the dues despite adequate cash flow and good net worth,
- Tapping off of funds to the detriment of the defaulting unit,
- Assets and proceeds have been misutilised;
- Misrepresentation / falsification of records;
- Disposal / removal of securities without bank’s knowledge;
- Fraudulent transactions by the borrower.
- The amount of wilful default must be of at least Rs. 25 lakhs as per the Central Vigilance Commission.
- Restrictions for wilful defaulters -
- Barred from participating in the capital market.
- Barred from availing of banking facilities for 5 years to start a new venture.
- Lenders are free to initiate the process of recovery with full ferocity and ay initiate criminal proceedings.
- Lending institutions do not allow any wilful defaulter to become a board member of any company.
- Barred from making an open offer.
The recent changes of RBI
- Applicable to – RBI expands the scope for regulated entities which can classify borrowers as wilful defaulters and broadens the definition of wilful default.
- These include, banks, Non-banking financial companies and all-India financial institutions and the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development.
- Time Limit - RBI said lenders need to complete classifying and declaring a borrower as a wilful defaulter within 6 months of the loan being classified as non-performing.
- NPA - Banks classify loans as bad or non-performing when repayments are delayed for over 90 days.
- Committee - The evidence of wilful default needs to be examined by an Identification Committee, to be set up by lenders.
- Limitations - The RBI also proposed that no additional credit facility be granted to a wilful defaulter or any entity by any lender with which a wilful defaulter is associated.
- The additional credit facility should be barred up to a year after the name of wilful defaulter has been removed from the List of Wilful Defaulters (LWD) by the lender.
- Settlement - The borrower has to settle the full amount if the lender has entered into a compromise settlement and the account included in LWD will be removed from the list.
- The lender should complete the investigation from a wilful default angle in every case before transferring the credit facility to other lenders or asset reconstruction companies (ARCs).
References
- The Indian Express | wilful defaulters
- Live Mint | Banks to tag wilful default
- Economic Times | wilful defaulter norms
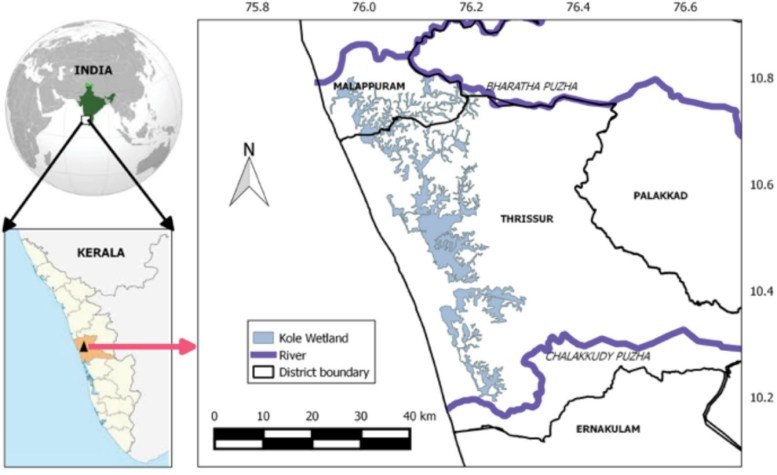
Kole Wetlands
Kole wetlands of Kerala face threat of alien plants recently.
- It is an internationally important Ramsar site of high value biodiversity situated in Kerala.
- The wetland gets its name from its high productivity Kole literally translates to bumper crop in Malayalam.
- It contributes to 40% of rice production in the state.
- It is one of the largest brackish, humid tropical wetland ecosystem on the southwest coast of India.
- The wetlands are fed by 10 rivers and is a typical large estuarine systems on the western coast.
- One of the specialties of this wetland cultivation is its dewatering scheme.
Dewatering is the process of removing groundwater and superficial water from a construction site.
- Each year, before the season starts, all farming clusters, known as padasekharams, have to follow dewater their land before sowing.
- This collaborative ritual or kootaima reeti is what protects Kole as a wetland.
Cabomba furcuta
- Cabomba furcuta is a species of aquatic plant in the water and is popularly called as Pink Bloom.
- Family - Cabombaceae.
- Habitat - It dominantly belongs to Central and South America.
- The submerged perennial aquatic plant grows in stagnant to slow-flowing freshwater.
- Threats - Due its massive flowering, has been a new threat to the kole fields, in addition to water hyacinth and Salvinia molesta.
- It is a visual treat and a potential outspread in water bodies by active stem propagation, hindering penetration of light into the water.
- Cabomba, which requires a large quantity of oxygen for its growth will choke water bodies and drainage canals.
- It causes decline in diversity of native aquatic plants and causes economic losses by affecting yield of freshwater fishes.

Reference
The Hindu | Kole wetlands of Kerala

