Reference
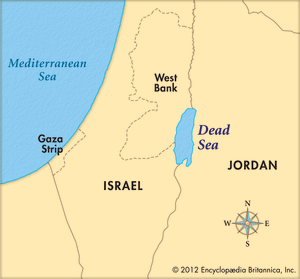
Thousands of sinkholes have formed around the Dead Sea, which has lost a third of its surface area since 1960.
Sinkholes are very common in limestone/karst areas.
Solution sinks are more common than collapse sinks.
Reference
INS Vela, the fourth Scorpene class submarine of Project 75 of the Indian Navy, was commissioned at the Indian Navy’s Western Command (Mumbai).
This will be the second addition to the Indian Navy’s fleet of warships after INS Vishakapatnam’s commissioning.
|
Name of the Submarine |
Commission Year |
|
INS Kalvari |
2017 |
|
INS Khanderi |
2019 |
|
INS Karanj |
2021 |
|
INS Vela |
2021 |
|
INS Vagir |
2020 (Still undergoing sea trials) |
|
INS Vagsheer |
Still in advanced stage of outfitting |
Reference
NITI Aayog under the Indo-German Cooperation releases the inaugural SDG Urban Index and Dashboard 2021–22

Reference
The Global State of Democracy Report, 2021 was released by the International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance (International-IDEA).
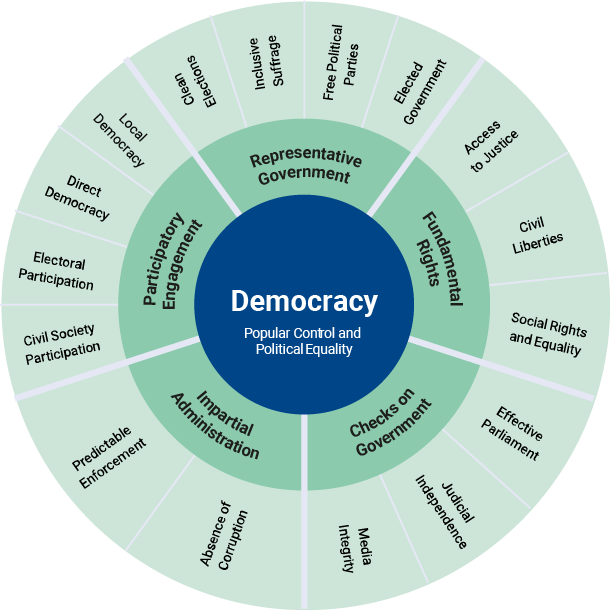
Number of countries moving towards authoritarianism in 2020 was higher than that of countries moving towards democracy.
Reference