World Energy Outlook
According to World Energy Outlook 2023, India will see the largest energy demand growth of any country or region in the world over the next 3 decades.
- It is the world’s most authoritative source of energy analysis and projections.
|
World Energy Outlook Report
|
|
Launched In
|
1998
|
|
Launched By
|
International Energy Agency (IEA)
|
|
Time Period
|
Annual
|
International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization established within the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Focus of the report
- Analysis current state of energy market.
- Evaluates energy transition.
- Assess environmental impact.
- Examines energy security, resilience and investment needs.
- Projects future energy demand, production and consumption.
The Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS) shows the trajectory based on current government policy, and those that are under development, around the world.
The Announced Pledges Scenario (APS) shows the trajectory if governments meet all aspirational climate targets on time.
Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE) maps out the trajectory required to achieve a 1.5°C world by 2030.
Findings of World Energy Outlook 2023 for India
- Power consumption – India will exceed the whole of Africa now.
- Air-conditioner usage – Residential ownership to see 9 fold increase by 2050.
- Energy demand – A sharp rise as temperatures cross the 25-degree Celsius threshold.
- Energy supply - To rise to 60.3 exajoules (EJ) by 2050.
- Investments – Need to nearly triple by the end of this decade to be on a trajectory to meet its net zero emissions target.
- Annual CO2 emissions – To rises nearly 30% by 2050, which is one of the largest increases in the world.
- Implication over India’s climate – Over the past 5 decades, more than 700 heatwave events occurred.
References
- The Hindu| World Energy Outlook 2023
- IEA| World Energy Outlook
CBDT’s data on Income Status
According to the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), India’s tax base has widened sharply since 2013-14, with individuals moving up the income ladder and the proportion of super-rich taxpayers’ incomes declining.
- Time Period – Assessment year (AY) 2013-14 to AY 2021-22.
- Increased tax base
- Income Tax (I-T) returns filing has almost doubled.
- As of now, current AY registered 53 lakh first-time tax filers.
- Filing saw 32% increase for gross total income up to ₹5 lakh.
- Migration to higher range of gross total income
- For income ranges of ₹5 lakh to ₹10 lakh, and ₹10 lakh to ₹25 lakh, the IT return filing surged 295% and 291% respectively.
- Average gross total income of taxpayers
- It increased from about ₹4.5 lakh to about ₹7 lakh representing an increase of 56%.
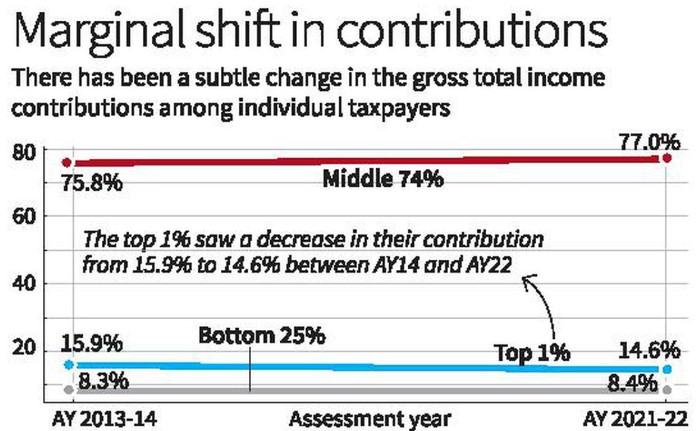
- The increase is 42% for top 1% and 58% for bottom 25% individual taxpayers.
- Changes in contribution of gross total income
- Declining trend observed among top 1% of taxpayers as their share decreased from 15.9% to 14.6% in the given period.
- Increased share of bottom 25% individual taxpayers which has risen from 8.3% to 8.4% in the given period.
- Increased share of middle 74% group of individual taxpayers from 75.8% to 77% in the given period.
Increased net direct tax collection
- It increase from ₹6.38 lakh crore in 2013-14 to ₹16.61 lakh crore in 2022-23, reflecting the robust growth in the gross total income of individuals across different income groups.
|
Central Board of Direct Tax
|
- It is a statutory authority functioning under the Central Board of Revenue Act, 1963.
- It deals with matters relating to levy and collection of direct taxes.
- It consists of a Chairman and 6 Members.
|
References
- The Hindu| CBDT’s Data on Income Status
- IncomeTaxIndia| CBDT
One Nation One Student ID (APAAR)
Recently, several state governments requested schools to seek parental consent for the creation of a new student identity card known as APAAR.
- APAAR – Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry is a special ID system for all students in India, starting from childhood.
- Each student would get a lifelong APAAR ID.
- Registration – It is voluntary, not mandatory.
- A consent form need to be signed by the student or parents in case of minors regarding the usage of their Aadhaar data which will be used to verify the name and date of birth.
- Umbrella programme – ‘One nation, One Student ID’, which stems from the NEP 2020.
- Objective
- To track academic progress from pre-primary to higher education.
- To serve as a gateway to Digilocker.
- To reduce fraud and duplicate educational certificates with a single, trusted reference for educational institutions.
Digilocker is a digital system where students can store their important documents and achievements digitally.
- Vision – To create a positive change by allowing state governments to track literacy rates, dropout rates, and many more.
- Working – Every student with APAAR ID be linked to the Academic Bank of Credit (ABC) to store certificates and credits.
Academic Bank of Credit (ABC) is a digital storehouse of information of the credits earned by students throughout their learning journey.
- On course completion, it is digitally certified and securely stored.
- Only 1st party sources will be allowed to deposit credits into the system, ensuring authenticity.
- On changing schools, the data in the ABC gets transferred to new school just by sharing the APAAR ID.
- Challenges – Privacy concerns related to students data. The government, however assures of confidentiality of shared information except for entities engaged in educational activities.
Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) database is the government’s catalogue that contains data related to schools, teachers and students.
References
Indian Express| One nation, One Student ID (APAAR)
Pichwai Painting
Chennai hosts an art exhibition, showcasing Pichwai, some dating back 350 years.
- It is also known as ‘pichvai’, one of the most spectacular and ancient forms of art.
- Origin - It is a 400-year-old art whose roots are from Nathdwara town in Rajasthan.
- Theme – It revolve around the various stages of Lord Krishna’s life, including his childhood, youth, and adulthood.
- Paintings – It is typically done on cloth, usually khadi but now being produced on various mediums such as paper, canvas, and silk.
- Different schools of Pichwai — Nathdwara, Kishangarh and Bundi in Rajasthan and Deccan school (relatively rare).
- Materials used – Use using natural colours made from minerals and plant extracts.
- Stone pigments are used for gold and silver tones.
- Vegetable dyes are used for brighter orange, red, chrome yellow and kesari colours.
- Usage – As a backdrop for hindu deities in temples.
- They are typically hung behind the idol of Shrinathji, a local form of Krishna and the centre of Pushtimarg worship.
- Popularity – It is known for their intricate details, ornate borders, and fine brushwork.

References
The Hindu| Pichwai Painting
Functional Haemoglobin in Cartilage
A recent study published in Nature, reported that chondrocytes (cells that make cartilage, the connecting tissue between bones) make haemoglobin and seem to depend on it for their survival.
- In a developing growth plate, oxygen is limited due to a lack of blood supply but still the chondrocytes manage to thrive.
Growth plates are the areas of new bone growth in developing stage which are made up of cartilage. Most growth plates are near the ends of long bones.
- Hedy or Haemoglobin bodies – Chondrocytes produce haemoglobin which coalesce to form large blobs of haemoglobin without a membrane.
- Absence of haemoglobin created some sort of low-oxygen (hypoxic) stress to chondrocytes.
- This confirms that hedy was most likely storing oxygen and supplying it to the chondrocytes when required.
- Thus it is essential for the survival of chondrocytes.
Haemoglobin in RBC
- A protein and the respiratory pigment found in red blood cells.
- It makes the blood red in colour and is the site of oxygen binding in the blood.
- Structure – It comprises 4 protein chains (2 alpha and 2 beta chains wherein each has a ring-like heme group which contains an iron atom).
- Function – It carries oxygen to the different tissues and organs of the body
- It also transports carbon dioxide from tissues and organs back to the lungs.
- Normal Haemoglobin level
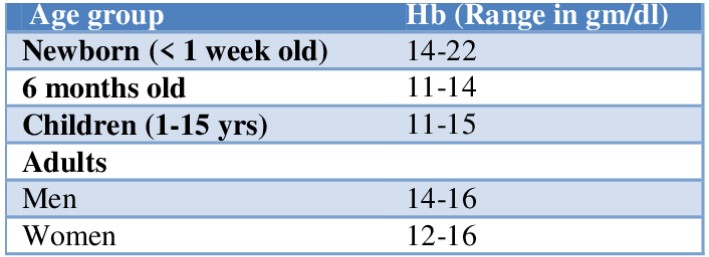
- Anaemia – Low haemoglobin levels usually indicate that a person has anaemia.
References
The Hindu| Haemoglobin in Cartilage


