900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
The Union Budget for 2023-24 announced an initiative for mangrove plantation along the coastline and on salt pan lands, under MISHTI (Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes).
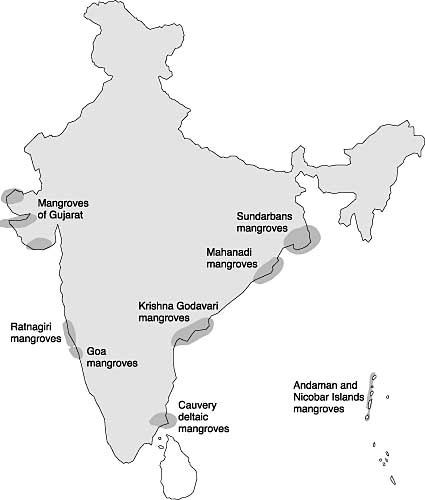
IFSR report points out that there has been an increase in the mangrove cover from 4,046 sq km in 1987 to 4,992 sq km in 2021.
Quick Facts
Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI)
References