900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Conference on Coastal Disaster Risk Reduction and Resilience (CDRR&R)
The Prime Minister’s 10-point Agenda
Sendai Framework for Disaster Reduction 2015-30
National Institute of Disaster Management
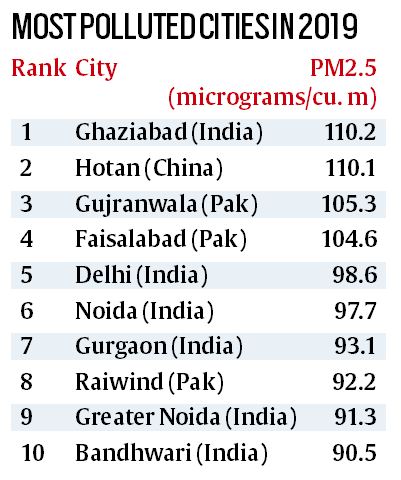
World Air Quality Report 2019
Elections to Rajya Sabha
E-court Integrated Mission Mode Project
National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG)
Olive Ridley Turtles
Rushikulya River
Source: PIB, Indian Express, the Hindu