900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
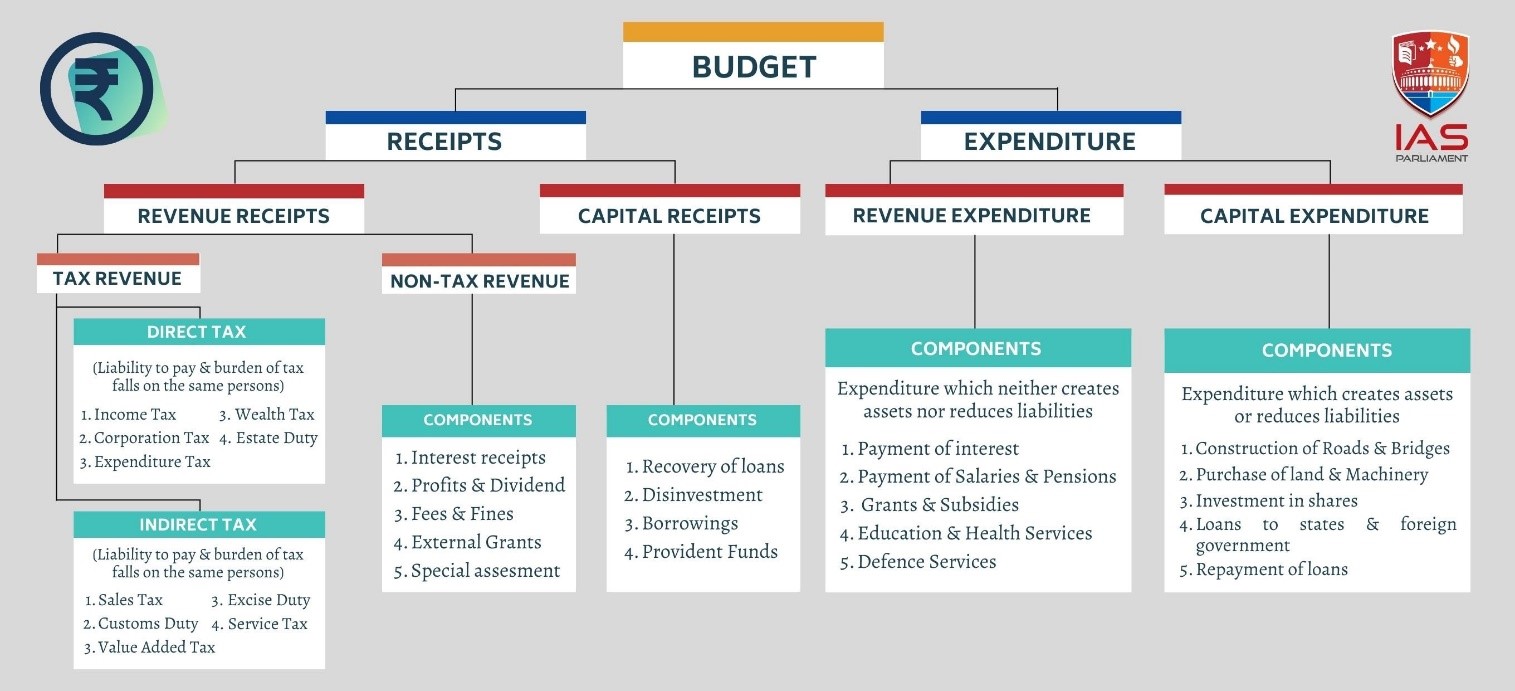
In the post pandemic fiscal strategy, the “golden rule” of targeting zero revenue deficit is gaining attention as a powerful mantra of fiscal discipline.
|
Related Terms |
|
|
Fiscal deficit |
|
|
Primary Deficit |
|
|
Revenue deficit |
|
|
Zero revenue deficit |
|
Fiscal marksmanship is known as the discrepancies between budgeted figures (Budget Estimates) and actual expenditure.
In the 2018 amendment to the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Rules 2004, the “golden rule” of zero revenue deficit was eliminated.
References