900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
As nations gather for the COP 28 in Dubai, the question of carbon capture’s future role in a climate-friendly world will be in focus.
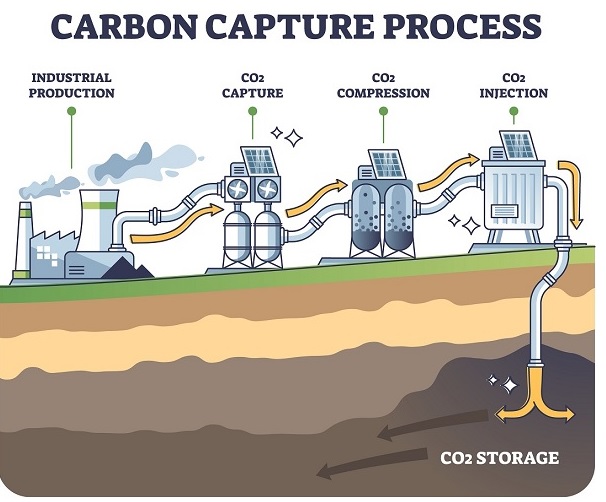
|
Process |
Examples |
|
Traditional process |
|
|
Technological process |
|
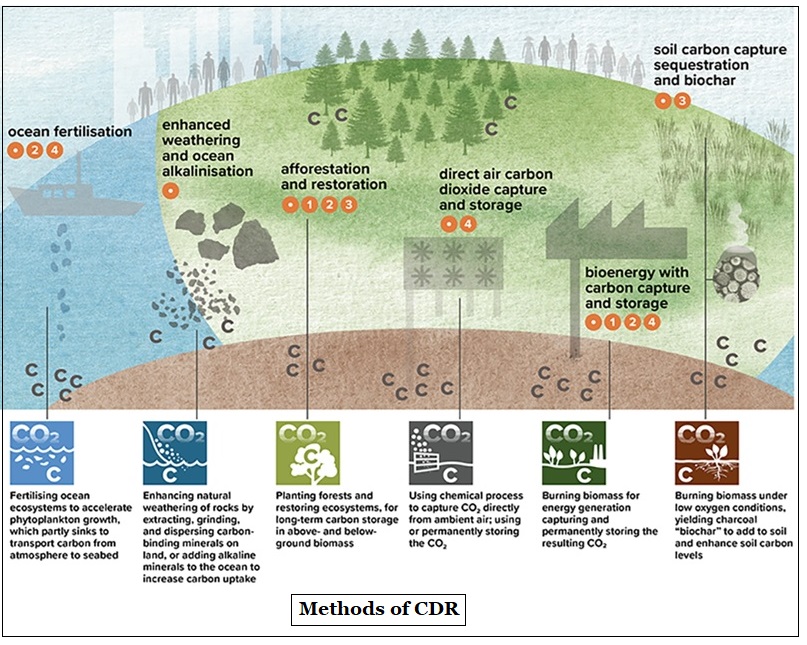
As of 2023, CDR is estimated to remove around 2 gigatons of CO2 per year, which is equivalent to 4% of the greenhouse gases emitted per year by human activities.
|
CDR method |
About |
Challenges |
|
Afforestation/ Reforestation |
|
|
|
Biochar |
|
|
|
BECCS |
|
|
|
DACCS |
|
|
|
Enhanced rock weathering |
|
|
|
Ocean alkalinity enhancement |
|
|
 What lies ahead?
What lies ahead?
References