900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
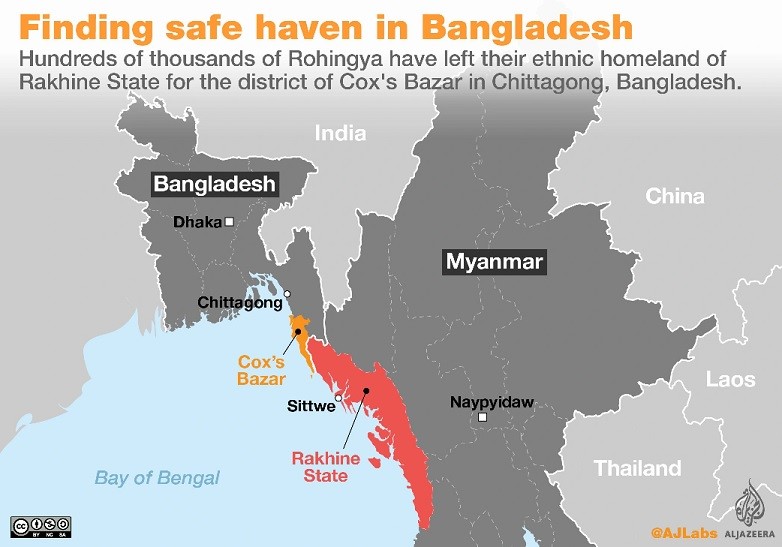
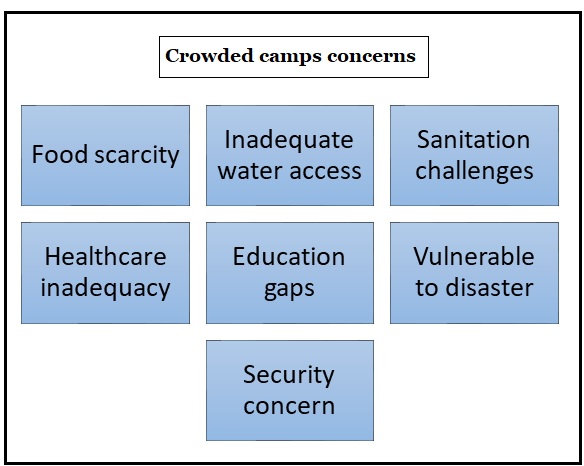
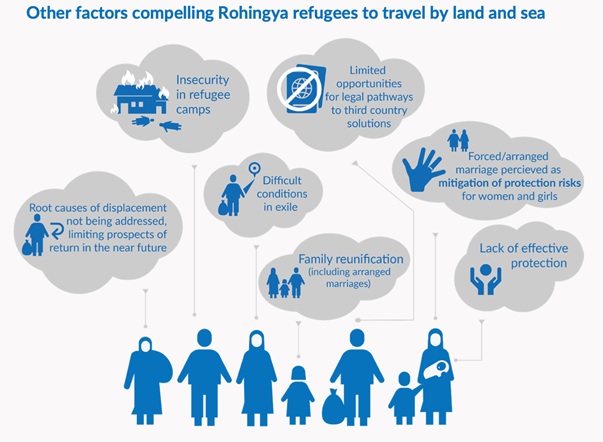
Recently Rohingya refugees are rescued in the waters of West Aceh, Indonesia has once again drawn attention to the plight of the refugees who are increasingly embarking on dangerous sea journeys to seek a better life.