In the Interim Budget 2024-25 the Centre announced that it would reduce its fiscal deficit to 5.1% of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2024-25.
It is the condition where the expenditure of the government exceeds its revenue in a financial year
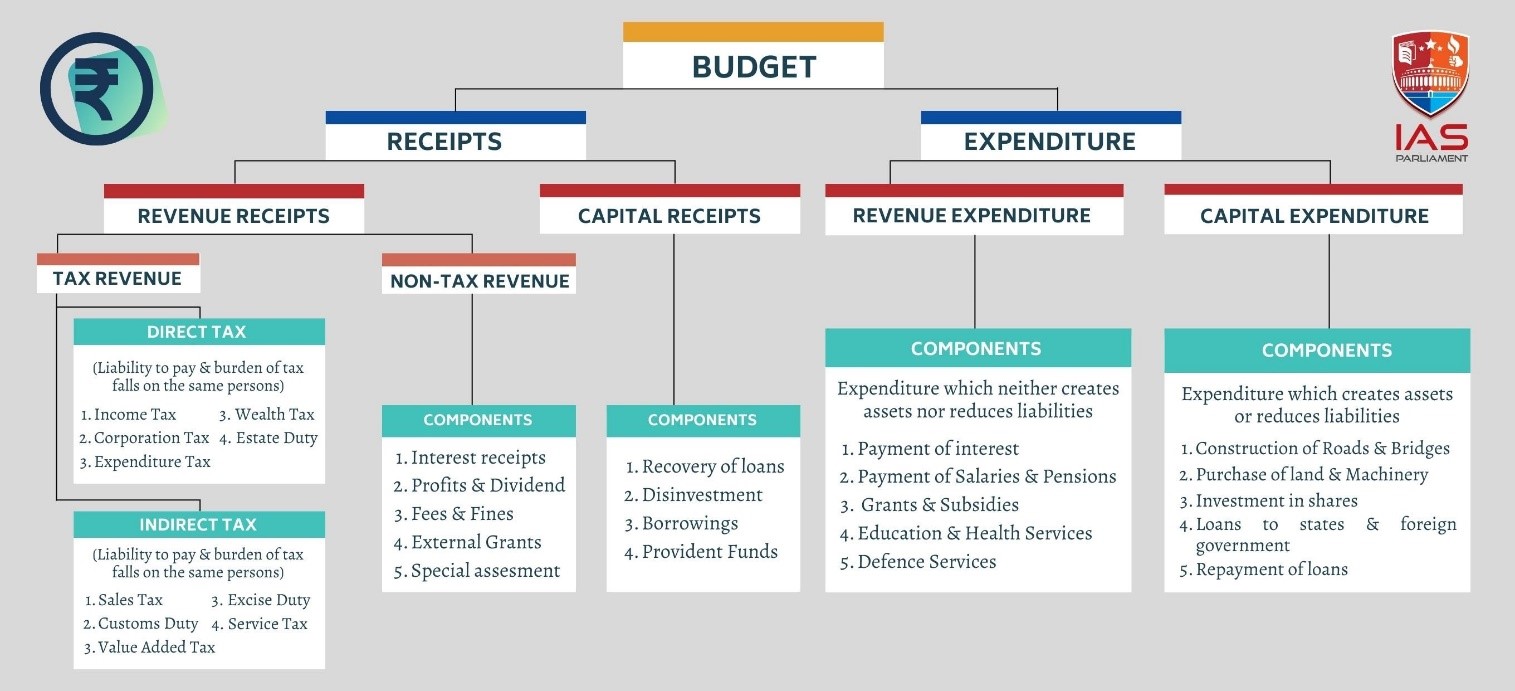
For the financial year 2023-24, the Indian government targeted a fiscal deficit of 5.9% of GDP.
|
Fiscal Deficit |
National Debt |
|
It focuses on the yearly budgetary gap between revenue and expenditure. |
It encompasses the total outstanding debt owed by the government over time. |
|
It is the annual measure. |
It is the cumulative borrowing history of the government. |
|
It is the amount by which the expenditure exceeds revenue. |
It accumulates over many years due to persistent fiscal deficits when the government spends more than it earns and borrows to cover the gap. |
To know about fiscal prudence click here
How the government fund its fiscal deficit?
Higher central bank rates makes it more expensive for the governments to borrow money from the market.
Why fiscal deficit is important?
Inflation is a rise in prices, which can be translated as the decline of purchasing power over time.
International Monetary Fund warned that India’s public debt could exceed 100% of GDP in the medium term due to associated risks.
What lies ahead?
Reference