Hindu Kush Himalaya
ICIMOD experts call for urgent finance to prevent collapse of nature in High Mountain Asia in a recent meeting at Kathmandu.
High Mountain Asia comprises of mountain ranges such as the Tian Shan, Kunlun Shan, Pamir, Karakoram, Hindu Kush, the Tibetan Plateau and the Himalayas. Mountains cover 22% of Earth’s land surface but hold 50% of the world’s global biodiversity hotspots.
- Geography – It stretches 3,500 kms and spans 8 countries, is home to most of the snow and ice on Earth outside the poles.
- It is located in Kathmandu (capital of Nepal).
- Importance – It comprises 4 biodiversity hotspots out of the world’s 36 global biodiversity hotspots, 2 of the global 200 eco regions, 575 Protected Areas, 335 important bird areas.
- Still 85% of mountain communities remain dependent on this biodiversity, for food, water, flood control and cultural identity.
|
Water Tower of Asia – Hindu Kush Himalayas
|
- It provides clean water for a third of the world’s population.
- At least 12 rivers fan out across the Asian continent from it.
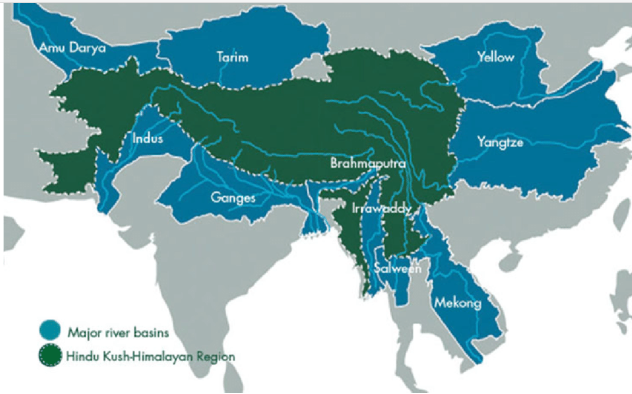 |
- Biodiversity on the brink – 70% of the original biodiversity has been lost over the last century.
- It is estimated to be warming at nearly 2 times the average rate of warming in the Northern Hemisphere.
- 241 million people live in the HKH region, of whom 31% are food-insecure and 50% of whom face some form of malnutrition.
The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), a regional intergovernmental organization established in 1983 to make Hindu Kush Himalaya region greener, more inclusive and climate resilient.
Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), an independent intergovernmental body established in 2012 for conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity. UNEP provides secretariat services to it.
References
- Down To Earth| Hindu Kush Himalayas is Deteriorating
- ICIMOD| Hindu Kush Himalayas
Conservation Reserve
The Telangana Forest Department moots conservation reserve in Tadoba-Kawal tiger corridor.
The proposed conservation reserve comprises areas of tiger corridor between the Tadoba-Andhrari Tiger Reserve in Maharashtra and the Kawal Tiger Reserve in Mancherial district of Telangana State.
- Conservation Reserve – A protected area that act as buffer zones to or connectors and migration corridors between established national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and reserved forests.
- Aim – To protect landscapes, seascapes, flora and fauna and their habitat.
- Legality – Wildlife (Protection) Amendment Act of 2002, the amendment to the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
- It is designated by the state government after discussing it with nearby communities.
- Criteria for designation – Uninhabited and completely owned areas of the Government.
- Managed by – Conservation Reserve Management Committee.
- 1 from each village panchayat.
- 3 from NGOs and 1 each from the departments of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry.
- A member-secretary who will be the representative from the Forest or Wildlife wing.
- Coverage – There are 115 existing Conservation Reserves in India covering an area of 5548.75 km2, which is 0.17% of the geographical area of India as of 2023.
The 1st conservation reserve of India is located near Tiruppadaimarathur in Tamil Nadu.
- Rajasthan has highest number of conservation reserves (36) followed by Jammu and Kashmir as on July, 2023.
Community reserves are protected areas which includes those areas owned by government but part of the lands are also privately owned.
References
- The Hindu| Conservation Reserve in Tadoba-Kawal tiger corridor
- ENVIS| Conservation Reserves in India
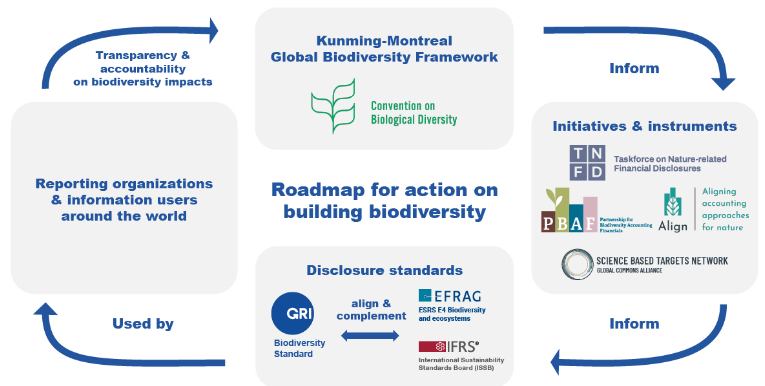
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Biodiversity Standard
An updated transparency standard to report a global response to the biodiversity crisis has been formed.
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) – An international independent standards organisation.
- Objective – To assists businesses, governments and other entities in assessing & reporting impacts, driving action and accountability on issues related to climate change, human rights and corruption.
- GRI Secretariat – Amsterdam, the Netherlands and have a network of 7 regional offices.
- Previous standard – GRI 304: Biodiversity 2016.
- GRI 101: Biodiversity 2024 – It updates, expands, and replaces GRI 304: Biodiversity 2016, effect from January 2026.
- Aim – To enable companies to meet the demands of stakeholders for information on biodiversity impacts and to understand the impacts of supply chain and operations.
Over 1 million plant and animal species being pushed towards extinction.
- Document design by – Global Sustainability Standards Board (GSSB), a group of consultants from representative organisations.
- Standards – It mentions location-specific impacts, direct drivers of biodiversity loss, and impacts on communities and Indigenous Peoples among others.
- Significance – It improves transparency on biodiversity impacts.
|
Biodiversity in UN Agenda for Sustainable Development
|
- SDG 14 – To conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources.
- SDG 15 – To protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss.
|
References
- Down To Earth| New GRI Biodiversity Standard
- Global Reporting| GRI
Nagoya Protocol
Recently, Cameroon has adopted the Nagoya Protocol.
Cameroon is a biodiversity hotspot, with an estimated 11,000 plant, animal, and microorganism species. Prunus Africana, a plant endemic to Cameroon, is used to make drugs for prostate cancer.
- Nagoya Protocol – A supplementary agreement to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) that came in 1993.
- Adopted in – 2010, in Nagoya, Japan and came into force in 2014.
- Objective – To ensure access of genetic resources and fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from their utilization, thereby contributing to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity.
- Coverage – It applies to genetic resources, associated benefits and traditional knowledge (TK) that are covered by the CBD.
- 3 core obligations – On access, benefit sharing and on compliance.
- Importance – It will create greater legal certainty and transparency for both providers and users of genetic resources.
- Both genetic resources and traditional knowledge are valuable for Bioprospecting.
Bioprospecting is the exploration of biological material for new sources of drugs, food or other products which can also help to conserve and sustainably use biodiversity.
- It also helps to protect the rights of indigenous and local communities and promote biodiversity-based innovation and development.
|
3 Objectives of Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
|
- The conservation of biological diversity
- The sustainable use of the components of biological diversity
- The fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources
|
References
- Down To Earth| Cameroon adopts Nagoya Protocol
- CBD| Nagoya Protocol
Magnetic Anomaly under Lake Rotorua
Recently, scientists have unveiled a hidden hydrothermal system and a magnetic anomaly beneath the waters of Lake Rotorua.
- Mapping Lake Rotorua's floor, showed a series of eruption craters, traces of an ancient river, and a significant magnetic anomaly in the southern part of the lake.
- Magnetic anomaly – Typically, volcanic rocks exhibit strong positive magnetic responses due to the presence of magnetite.
- But in Lake Rotorua, the hydrothermal fluids have altered the magnetite into pyrite, or fool's gold.
- This results in a reduced magnetic signal.
|
Lake Rotorua
|
- Geography – It is situated atop a dormant volcanic crater on New Zealand's North Island.
- Formation – When a magma chamber collapsed following a volcanic eruption, created the Rotorua Caldera.
- Characteristics – It is shallow, with an average depth of about 10 m, and is part of the Taupo Volcanic Zone.
- It is renowned for its geothermal marvels such as bubbling mud pools, shooting geysers, and natural hot springs.
- But despite the intense geothermal activity, its temperature at the bottom remains cooler.
|
- Significance of discovery – It confirm for the 1st time that the hydrothermal activity on the mainland extends into the submerged realm of Lake Rotorua.
- It helps to deepen our understanding of the complex interplay between land, water, and the forces beneath the Earth's crust.
Reference
India Today| Magnetic Anomaly under Lake Rotorua
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
MERA GAON MERI DHAROHAR (MGMD)
|
|
The Government of India has decided to map and document all villages under Mera Gaon, Meri Dharohar (MGMD) Programme.
- The Mera Gaon, Meri Dharohar (MGMD) Programme is a National Mission on Cultural Mapping.
- The Ministry of Culture is conducting the program in collaboration with the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA).
- The program will create a virtual platform that allows people to explore India's cultural heritage.
|
|
High-speed Expendable Aerial Target ‘ABHYAS’
|
|
4 Four flight trials of High-speed Expendable Aerial Target (HEAT) ABHYAS were successfully carried out by Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) recently.
- ABHYAS – The High-speed Expendable Aerial Target (HEAT) ABHYAS is a high-speed indigenously-designed target developed for the Indian Armed Forces.
- It is designed for autonomous flying with the help of an auto pilot made by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
|
|
E-SAKSHI
|
- It was launched for revised fund flow procedure under Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS).
- Launched by – Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- It offers convenience and accessibility, allowing MPs to propose, track, and oversee the projects in real-time and enabling swift responses to emerging needs or issues.
|
|
Robotic Elephant
|
- A robotic elephant was handed over to the Shivan Temple in Devarshola in Gudalur, Tamil Nadu by an NGO recently.
- The aim was to ensure traditions involving elephants could still be continued, but without the actual animals, who deserved to live in the wild.
|
|
OBC Reservation Bill in Jammu & Kashmir
|
|
The Union government recently introduced a Bill in the Lok Sabha to provide reservation to Other Backward Classes (OBCs) in panchayat and municipal bodies of Jammu and Kashmir.
- The number of seats reserved for OBCs will be decided by a commission that will be formed after the legislation has been passed by the Parliament.
- Presently, there is no reservation for OBCs in panchayats and municipalities in the Union Territory.
|
|
Dhanauri wetland
|
- The Dhanauri Wetlands & birdwatching area is located in Dhanauri village in Uttar Pradesh.
- The Dhanauri Wetland is a vital birding and nesting site for more than 217 bird species, including over 150 Sarus cranes (State Bird of U.P.)
- It is also home to 23 species of endangered, critically endangered, and threatened birds.
- The wetland is an Important Bird Area recognized by Bird Life International and has been documented by the Bombay Natural History Society.
|
|
Astronomical Society of India
|
|
Bengaluru will host the largest annual gathering of astronomers from India when the 42nd meeting of the Astronomical Society of India will be held in the capital of Karnataka.
- The Astronomical Society of India was established in 1972 and has grown to become the prime association of professional astronomers in India.
- The objectives of the society are the promotion of Astronomy and related branches of science in India.
- The society organizes scientific meetings and supports the popularization of Astronomy and other similar activities.
|
|
Brown Wood Owl (Strix leptogrammica)
|
- The brown wood owl is found in India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Taiwan, and south China.
- It is a resident breeder in south Asia.
- These owl species do not have ear tufts and have high forest dependence and are polytypic species (contains two or more subspecies).
- Conservation status
- IUCN - Least Concern
- CITES - Appendix II
|
|
Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY)
|
- PMKKKY is meant to provide for the welfare of areas and people affected by mining related operations.
- It will be implemented by the District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) of the respective districts using the funds accruing to the DMF.
|
|
Lunar Nuclear Fission Reactor
|
|
NASA finishes 1st phase of ambitious lunar nuclear reactor project recently.
- Solar power has its limitations on the Moon because night on Earth’s lone satellite lasts for the equivalent of 14 days here on Earth.
- But a nuclear reactor, even one placed in permanently shadowed areas where there might be water ice, could generate power continuously without any dependence on weather.
|

