|
Other Important News
|
|
Digital Criminal Case Management System (CCMS)
|
|
Union Home Minister has launched a unique Digital Criminal Case Management System (CCMS) Platform recently.
- About - It is a browser-based software to help the State Police forces in their investigations and prosecution.
- Designed by - National Investigation Agency (NIA).
- Significance - Enable the NIA personnel to better co-ordinate in terrorism and organized crime cases, thereby improving justice delivery.
Sankalan App
- About - Collection of new criminal laws by National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
- Significance - Designed for navigating through new criminal laws as a bridge between old and new criminal laws.
- Enables the users to run the application on offline mode.
|
|
Personalities in News
|
|
Sheena Rani
- A distinguished scientist from Hyderabad-based Advanced Systems Laboratory (ASL) of Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO).
- She led a DRDO team for Mission Divyastra, India's maiden flight test of the Agni-5 missile equipped with MIRV technology.
- She was awarded with the prestigious “Scientist of the Year” award in 2016.
Gyanesh Kumar & Sukhbir Singh Sandhu
- Gyanesh Kumar, Sukhbir Singh Sandhu were appointed as Election Commissioners (ECs).
- Selection Committee of ECs - Prime Minister, Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and a Union Cabinet Minister to be nominated by the Prime Minister.
|
|
RBI's Gold Imports
|
|
India has recently allowed RBI to import gold without paying import levies.
- Generally, import of gold attracts 15% import duty, including 5% agriculture infrastructure development Cess.
- According to the World Gold Council data, the RBI has a gold holding of 812.3 tonne in January 2024.
- Of that, 388.06 tonnes is held overseas and 372.84 tonnes is held domestically.
- Need- To diversify the forex reserves and hedge against foreign currency risks
Agriculture Infrastructure and Development Cess (AIDC)
- It is a tax on the commercial production of agricultural goods in India.
- A cess is a form of tax levied by the government on tax with specific purposes till the time the government gets enough money for that purpose.
- It was announced on certain items, including petrol, diesel, gold and some imported agricultural products to boost agriculture infrastructure.
|
|
Lamphelpat Lake
|
|
Lamphelpat Lake is now undergoing a remarkable revival under Lamphelpat Waterbody Project.
- Lamphelpat - A natural lake in Manipur located in the foothills of the Langol hill range.
- It served as a reservoir, storing excess water of the Luwangli and Nambul rivers.
- The lake is considered a mini Loktak lake that maintains the ecosystem of Imphal and its surrounding areas.
- Loktak Lake – Located in Manipur, it is the largest freshwater lake in Northeast India
- Lamphelpat Waterbody Project - Initiated by the Manipur Water Resource Department in collaboration with the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- It has 6 major components that includes flood control, drainage management and promotion of ecotourism.
|
|
Miassite (Rh17S15)
|
|
Scientists have recently identified the 1stunconventional superconductor, Miassite that can be found in mineral form in nature.
- Miassite is one of only 4 minerals found in nature that act as a superconductor when grown in the lab.
- It is an unconventional superconductor with properties similar to high-temperature superconductors.
- Superconductivity is when a material can conduct electricity without energy loss.
- London penetration depth test was used to identify the type of superconductivity present in miassite.

|
|
Global Connectedness Report, 2024
|
- By - DHL and New York University’s Stern School of Business
- It ranked the connectedness of 181 countries, accounting for 99.7% of the world’s gross domestic product.
- India’s Ranking - India ranks 62nd out of 181 economies, based on 2022 data tracking global flows of trade, capital, information and people.
- Breadth of merchandise trade (reach of India’s exports and imports across global markets) – Ranks 9
- Depth of merchandise trade (size of India’s international flows relative to its domestic activity) – Ranks 161
|
|
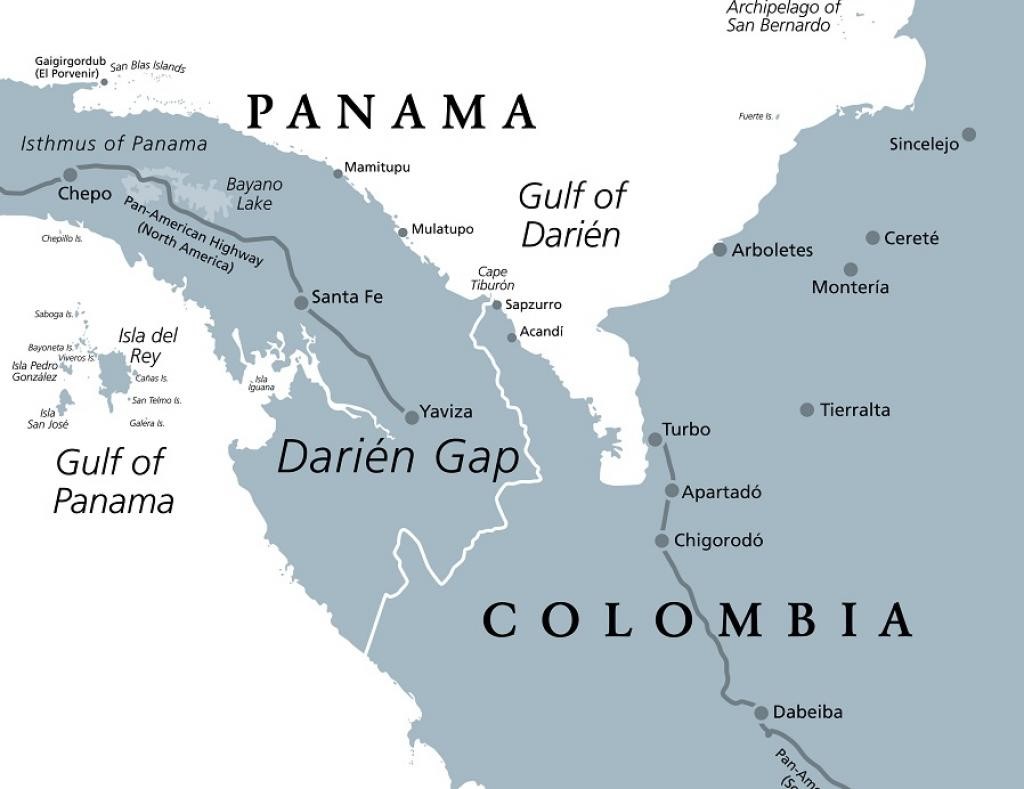
Darien Gap
|
|
A record 520,000 people crossed the Darien Gap in 2023.
- It is a stretch of densely forested jungle across northern Colombia and southern Panama around the Gulf of Urabá.
- It forms the physiographic link between Central and South America.
- It is a hot, humid area typified by tropical rainforests, mangrove swamps, and low mountain ranges with cloud forest vegetation.
- No paved roads exist in the Darien Gap but it has become a major route for global human migration.
- The Missing Migrant Project reported 141 known deaths in the Darien Gap in 2023.
- Darien National Park in Panama and Los Katios National Park in Colombia finds mention in the UNESCO World Heritage List.
|
|
Old-growth forests
|
|
Sweden has vast ‘old growth’ forests but they are being chopped down faster than the Amazon.
- Old-growth forests are forests that have developed over a long period of time without disturbance.
- They are also known as primary forests, virgin forests, primeval forests, late seral forests, or ancient woodlands.
- They are exceptionally valuable as they tend to host more species, store more carbon, and are more resilient to environmental change.
- Forests cover approximately 31% of the total global land area out of which roughly one-third is old-growth forest.
- More than half of the world’s old-growth forests are found in Brazil, Canada, and Russia.
- Examples of old-growth forests - California redwoods, Tongass National Forest in Alaska, and Adirondack forests in New York.
|
Clear-cutting is the practice of cutting down most or all of the trees in a forest at once.
|
|
|
Neonatal deaths
|
|
The recent report by United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation noted that the annual number of global under-5 deaths in 2022 declined by more than half.
- Neonatal deaths - Number of deaths during the first 28 completed days of life per 1000 live births in a given year or other period.
- Classification
- Early neonatal deaths - Occur within the first 7 days of life.
- Late neonatal deaths- Occur between 7 to 28 days.
- Causes -Preterm birth, low birthweight and birth defects.
- Globally, neonatal deaths happened every 14 seconds, a child aged under 5 died every 6 seconds and an adolescent died every 35 seconds in 2022.
United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (UN IGME)
- UN IGME is a technical group that produces annual estimates of child and adolescent mortality.
- It was established in 2004 to share data, improve methods, and report on progress towards child survival goals.
- The UN IGME includes representatives from UNICEF, WHO, the World Bank, and the United Nations Population Division.
|
|
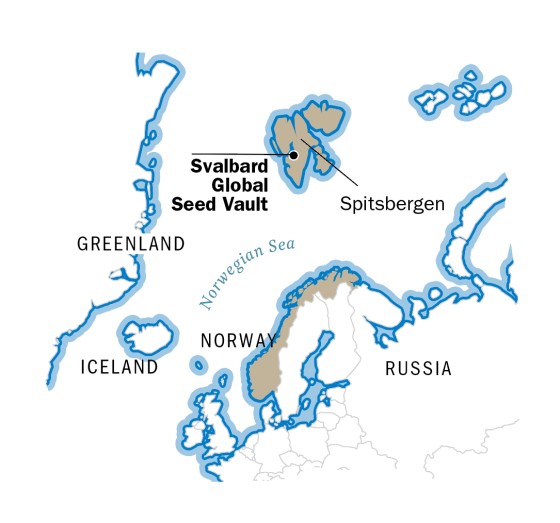
Global Seed Vault
|
- Location - Spitsbergen, part of Norway’s Svalbard archipelago.
- It stores millions of seed samples from around the world and is only accessible 3 times a year.
- Also known as “doomsday” vault, as the reserve of seeds can be of use in case of an apocalyptic event or a global catastrophe.
- The facility was built in 2008 with assistance from the Norwegian government and the Global Crop Diversity Trust.
- It is part of the international system for conserving plant genetic diversity guided by the UN organisation for Food and Agriculturen (FAO).
The Arctice World Archive that aims to preserve data for the world’s governments and private institutions is also located in Spitsbergen, Norway.
|