Cantor's Giant Softshell Turtle
A team of conservationists, uncovered the nesting site of Cantor's giant softshell turtle on banks of the Chandragiri River in Kerala.
- It is the 1st breeding site that has been discovered in India.
The Chandragiri River also known as the Perumpuzha River, is the longest river in Kasaragod district in Kerala. River Payaswini is its tributary.
- Scientific name – Pelochelys cantorii
- Nativity – It is native to the rivers of South and Southeast Asia, including Bangladesh, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia and India.
- It is also called Asian giant softshell turtle.
- Habitat – Mainly inland, slow-moving, freshwater rivers, lakes, streams, and estuaries but also extends to coastal areas.
- Features – It is an exceptionally large freshwater turtle, which reach over 1m in length and weigh more than 100 Kgs.
- It has broad head with eyes close to the tip of the snout, a frog-like appearance and so the name ‘Frog Head Turtle’.
- They are primarily carnivores (piscivores) feeding on fish, crustaceans, and mollusks but may also eat some aquatic plants.
- Secretive Nature – Mostly, they lie buried and motionless, with only their eyes and mouth protruding from the sand.
- They surface only twice a day to take a breath and capture their prey by sit-and-wait strategy using an element of surprise.

- Threat – Harvesting by local people for meat, accidental killing and persecution from fishermen when caught in fishing gear, and the destruction of its freshwater and coastal habitats.
- Protection status
- IUCN – Critically Endangered (CR)
- CITES – Appendix II
- Wildlife Protection Act,1972 – Schedule 1
References
- BBC| Discovery of Cantor’s Giant Softshell Turtle
- Animalia| Cantor’s Giant Softshell Turtle
International Mother Language Day (IMLD)
Recently, International Mother Language Day 2024 was celebrated worldwide.
- International Mother Language Day – On February 21, every year globally.
- Started from – 2000, as a commitment towards understanding the importance of the mother language or mother tongue.
- Aim – To recognise and promote linguistic & cultural diversity and multilingualism.
- Historical background – It was initiated by Bangladesh, to commemorate a 1952 protest against West Pakistan’s imposition of Urdu as the official language in present-day Bangladesh.
- It was approved by UNESCO in 1999, and the UN General Assembly welcomed it in its resolution of 2002.
UN General Assembly proclaimed 2008 as the International Year of Languages to promote unity in diversity and international understanding, through multilingualism and multiculturalism.
- Significance – It is a cornerstone for achieving equitable access to education and lifelong learning opportunities for all individuals.
- It shows benefits in fostering better learning outcomes, self-esteem, and critical thinking skills and also supports intergenerational learning and cultural preservation.
- It promotes inclusive societies and also aids in preserving non-dominant, minority, and indigenous languages.
- Threat – Currently, 40% of the global population lacks access to education in their native language, it exceeds 90% in certain regions.
- Every 2 weeks a language disappears taking with it an entire cultural and intellectual heritage.
- At least 45% of the estimated 7000 languages spoken in the world are endangered.
The theme of International Mother Language Day 2024 is ‘Multilingual education is a pillar of intergenerational learning’.
|
Oldest Languages in India
|
|
Urdu
|
Over 700 years
|
|
Hindi
|
Over 800 years, with over 422 million speakers
|
|
Gujarati
|
Over 100o years
|
|
Bangla
|
Over 1500 years
|
|
Marathi
|
About 1500-2000 years, with 71.9 million speakers
|
|
Telugu
|
About 1500-2000 years
|
|
Odia, Kannada & Malayalam
|
Over 2000 years
|
|
Sanskrit
|
Over 3000 years
|
|
Tamil
|
Over 5000 years
|
References
- NDTV| Celebration of International Mother Language Day 2024
- UN| Background of IMLD
- Times of India| India’s Oldest Languages
Nilgiri Marten
Tamil Nadu Government has planned to conserve the lesser-known species such as Nilgiri Marten under its new “TN Endangered Species Conservation Fund”.
- It is a rare species of marten, a small carnivores belonging to the weasel and badger families.
The Nilgiri marten is the only marten species native to India.
- Scientific name – Martes gwatkinsii
- Native – Endemic to the Western Ghats.
- Distribution – It spans across the states of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu.
- Habitat – 5 clusters in the Western Ghats namely Brahmagiri, Nilgiris, Anamalai, Cardamom Hills and Agasthyamalai.
- They are seen in Shola ecosystems, typically semi-evergreen forests, evergreen forests and forest patches interspersed with grasslands and also in tea, acacia, coffee, cardamom, and wattle plantations.
- Features - It is a small mustelid with a chocolate coloured fur and a canary yellow throat.
- It looks like a civet or a mongoose and it most prefers higher altitudes (300 to 1200 m).

The Mustelidae are a diverse family of carnivorous mammals, including weasels, stoats, badgers, otters, martens, grisons, and wolverines.
- Life style – They are omnivorous, diurnal, and mainly arboreal but descend to the ground occasionally.
- They are social and spend their time and even hunt in groups.
- Threats – Habitat loss & fragmentation and poaching.
- Protection status
- IUCN Status - Vulnerable
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 - Schedule II
TN Endangered Species Conservation Fund is 1st of its kind fund in India for Endangered Species. With an initial corpus of Rs. 50 crore, it aims to protect and recover lesser-known species facing extinction threats.
References
- India Today| Need to Conserve Nilgiri Marten
- Animalia| Nilgiri Marten
Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH)
Recently, a digital health platform ‘Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH)’ was launched as agreed upon in India’s G20 presidency in 2023.
Digital health refers to use of digital tool and technologies to improve health and provide better health care delivery. It is a proven accelerator to advance health outcomes and achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and health-related Sustainable Development Goals.
- Launched in – 2024
- Launched by – World Health Organisation (WHO)
- It is a WHO Managed Network (Network of Networks), to promote equitable access to digital health.
- Need – There is fragmentation and overlap because new tools are built without following common standards or shared vision and we need system to communicate with different digital health devices.
- Objectives – To assess and prioritize country needs for sustainable digital health transformation by aligning country-level digital health resources.
- To support the accelerated achievement of the strategic objectives of the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025.
- To build capacity and converge efforts to encourage local development, maintenance, and adaptation of digital health technologies to continuously changing needs.
- Membership – Open to all institutions engaged in digital health.
Over 120 WHO Member States have developed a national digital health policy or strategy.
- Annual operating Budget – 14 million USD
- 4 foundational pillars
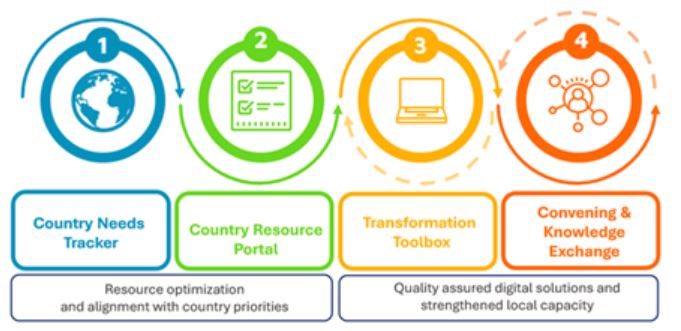
- 3 ways of supporting – By listening to their needs, by aligning resources to avoid fragmentation and overlap, and by providing quality assured products.
- Significance – It will help in democratising digital health technologies, especially for countries of the Global South.
While nearly half the world’s population might not have access to health services they need, nearly 90% have access to a 3G connection showing the potential for digital health.
|
India in Digital Health
|
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission – It works towards creating a seamless electronic health record system in India.
- E Sanjeevni – A teleconsultation platform provided 140 million consultations so far.
- CoWIN platform – It tracked COVID cases digitally along with managing the largest vaccination drive by issuing digital, verifiable vaccination certificates.
|
References
- The Indian Express| WHO launches GIDH
- WHO| Global Initiative on Digital Health
Badwater Basin
The recent images of NASA shows that Badwater Basin, the driest place in North America has been home to a lake for 6 months.
- It is an endorheic basin with a depth of 282 feet below sea level.
- Location – Death Valley National Park, Death Valley in USA.
Death Valley is well-known as the hottest place on Earth and the driest place in North America and is essentially a dry salt flat.
- Lake formation – Being endorheic in nature, it allows water flows into it but not out, typically resulting in rapid evaporation and ephemeral lakes.
- Manly lake – It was formed in August 2023 after Hurricane Hilary.
- While the lake initially shrank as expected, it surprisingly persisted through the fall and winter months.
- Its resurgence came in February 2024, when a powerful atmospheric river replenished its waters.
- At its largest, it was about 11 kms long, 6.5 km wide and about 60 cm deep.
- It now fills the low-lying salt flat, sspanning several kilometers.

Quick Facts
- Basin – A depression, or dip, in the Earth's surface which are shaped like bowls, with sides higher than the bottom.
- Ephemeral lakes – They are basins that remain flooded for short periods of time during a year but may not hold water for several years if the rainfall regime is not suitable to produce flooding.
- Atmospheric River – A relatively narrow plume of moisture that forms over an ocean and can produce intense rainfall or snowfall when it reaches land.
Reference
Down To Earth| Manly Lake formation in Badwater Basin
|
Other Important Topics
|
|
Kalpana
|
|
Skyroot Aerospace, an Indian private aerospace manufacturer, has launched the Kalpana fellowship for women interested in space tech.
- This new program is India's first fellowship exclusively dedicated to empowering women engineers in the realm of space technology.
- It is named in honor of the late astronaut Kalpana Chawla.
- It is open to final year students and recent graduates in relevant engineering disciplines.
|
|
Pigeonpea
|
|
The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) has created the world's 1st Pigeonpea speed breeding protocol to reduce breeding cycle of Pigeonpea by 3-5 years.
- Scientific name - Cajanus cajan; Family - Fabaceae
- India ranks 1st in area and production of Pigeonpea.
- The state-wise trend shows that Maharashtra ranks 1st both in area and production.
- It is also called as arhar, tur or red gram.
- It has low glycaemic index and is rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Traditionally, Pigeonpea breeding can take up to 13 years.
- After gram, Pigeonpea is the 2nd most important pulse crop in the country.
|
|
Iraq's Rivers
|
|
Stricken by drought and depleted by upstream dams, Iraq's rivers - the Tigris and Euphrates are suffocating under pollutants.
- Tigris - It flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the Persian Gulf.
- Surrounded by 4 countries (Iran, Iraq, Turkey, and Syria), the Tigris River is the second largest river in western Asi a.
- Originating in Lake Hazer in Turkey, the river flows parallel to the Euphrates River.
- Euphrates - It is the longest river in the Southwest Asia.
- The river rises in Turkey and flows southeast across Syria and through Iraq and then empties into the Persian Gulf.
- Tigris and Euphrates makes up a river system that borders Mesopotamia in the area known as the Fertile Crescent.
Iraq is known as the “land of two rivers”.

|
|
Mundra Port
|
|
To bypass Red Sea, new trade route to Israel involving Mundra port was suggested by Israeli Transport Minister.
- It is India’s largest commercial port.
- It is a flagship facility of Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone (APSEZ).
- It is located in the district of Kuchchh, Gujarat.
- In the new route, goods move from Mundra to ports in the UAE, such as Dubai’s Jebel Ali Port and then through Saudi Arabia and Jordan to Israel.

|
|
Safety of Women
|
|
Cabinet approved the proposal of Ministry of Home Affairs of continuation of implementation of Umbrella Scheme on ‘Safety of Women’ during the period from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Emergency Response Support System (ERSS) 2.0;
- Upgradation of Central Forensic Sciences laboratories, setting up of National Forensic Data Centre;
- Strengthening of DNA Analysis, Cyber Forensic capacities in State Forensic Science Laboratories (FSLs);
- Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children;
- Capacity building and training of investigators and prosecutors in handling sexual assault cases against women and children;
- Women Help Desk & Anti-human Trafficking Units.
|
|
Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)
|
|
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approves ‘Fair and Remunerative Price’ (FRP) of sugarcane for 2024-25 at Rs. 340 per quintal at sugar recovery rate of 10.25%.
- FRP is the minimum price to be paid by sugar mills to farmers for buying sugarcane.
- The FRP has been determined on the basis of recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- The new FRP is 107% higher than A2+FL cost (Includes value of unpaid labour of family workers in addition to A2) of sugarcane.
- Sugarcane is grown mainly in Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, and Karnataka.
- It is based on the Rangarajan Committee report of reorganizing the sugarcane industry.
|
|
Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC)
|
|
Union Finance Minister chairs the 28th meeting of Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) in New Delhi.
|
|
World Day of Social Justice 2024
|
|
The World Day of Social Justice is observed every year on 20th February
- The UN General Assembly has declared the World Day of Social Justice in 2007.
- The theme for the year 2024 - Bridging Gaps, Building Alliances.
- This day is dedicated to promoting social justice and ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to reach their full potential.
|
|
Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP)
|
|
The Union Cabinet has recently approved the Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP) for the period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme that supplements the efforts of the State Governments in flood management.
The scheme has two components:
- Flood Management Programme (FMP) Component - Central assistance is provided to State Governments and the expenditure on these schemes are shared between the centre and state.
- River Management and Border Areas (RMBA) component - Taken up with 100% central assistance.
The scheme was initially launched during XI plan & has continued thereafter.
|