900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
Recently, Home Minister has said that members had complained about the inclusion of their names in the proposed Select Committee without their signatures.
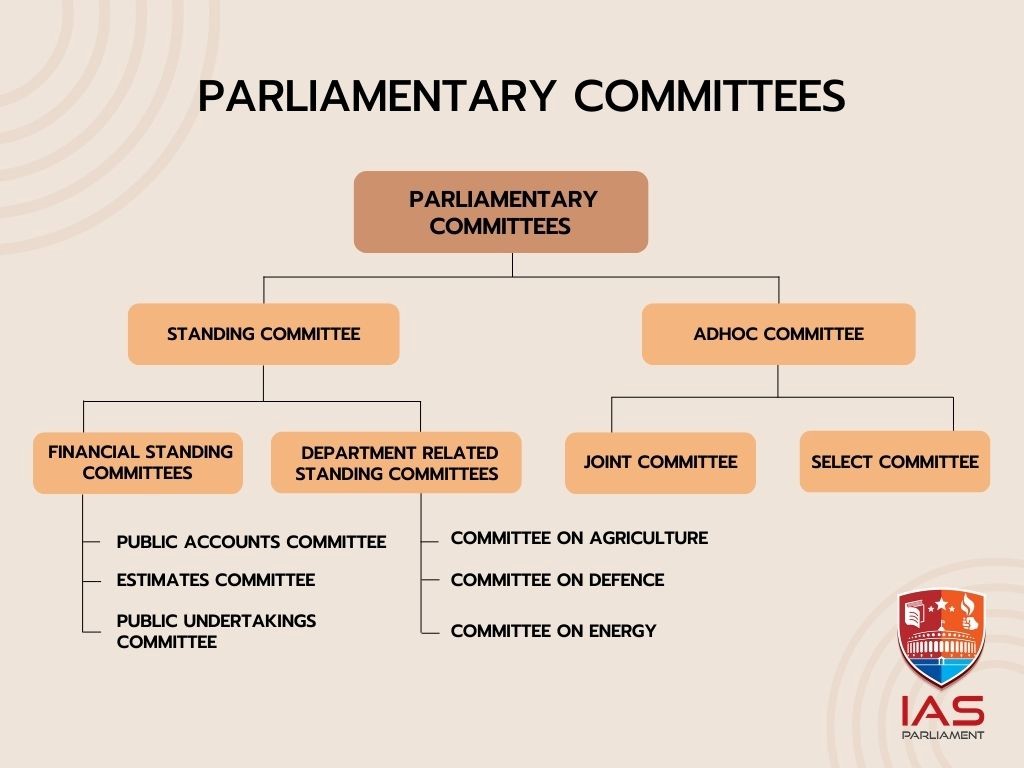
There is no provision for joint sitting on a money bill or a constitution amendment bill.
Reference