900 319 0030
enquiry@shankarias.in
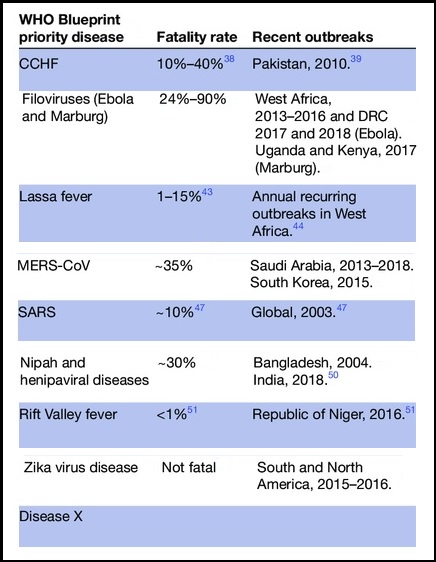
The WHO Director-general at the 76th world health assembly has cautioned against the threat of emerging pathogens.