MoEFCC is the nodal agency for planning, co-ordination and overseeing the implementation of India’s environmental and forestry policies and programmes.

Updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
|
About |
First NDC in 2015 |
Updated NDC |
|
Emission intensity of its GDP |
To reduce 33-35% from 2005 levels |
To reduce 45% by 2030 from 2005 levels |
|
Non fossil fuel based energy |
40% |
To achieve 50% by 2030 |
Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI)
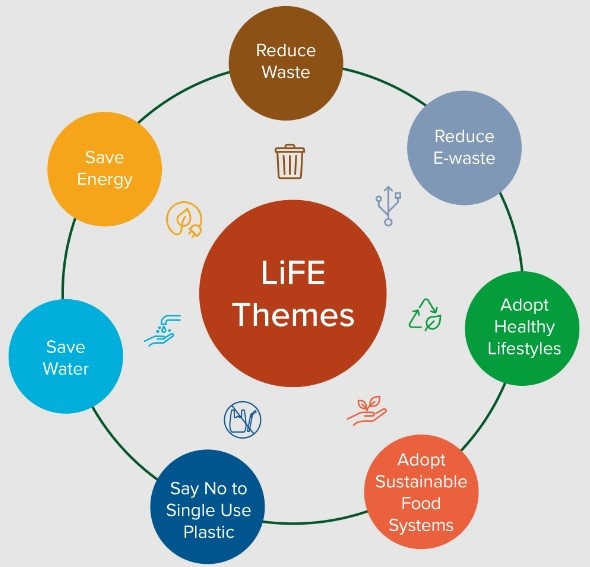
Mission LiFE (Lifestyle For Environment)

International Big Cat Alliance
Indira Parayavaran Bhawan
India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021
|
Aspects |
Top 3 States |
|
Area-wise largest forest cover |
Madhya Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh and Chhattisgarh |
|
Forest cover as % of total geographical area |
Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh and Meghalaya |
|
Increase in forest cover |
Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Odisha |
PARIVESH 2.0
|
List of wetlands recently added to the Ramsar Sites |
|
|
Koonthankulam Bird Sanctuary |
Tamil Nadu |
|
Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve |
|
|
Vembannur Wetland Complex |
|
|
Vellode Bird Sanctuary |
|
|
Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary |
|
|
Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary |
|
|
Nanda Lake |
Goa |
|
Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary |
Karnataka |
|
Sirpur Wetland |
Madhya Pradesh |
|
Satkosia Gorge |
Odisha |
Amrit Dharohar Yojana has been launched for conservation of Ramsar sites through community participation.
|
Government Initiatives for Wetland Conservation |
|
Forest (Conservation) Amendment) Act, 2023
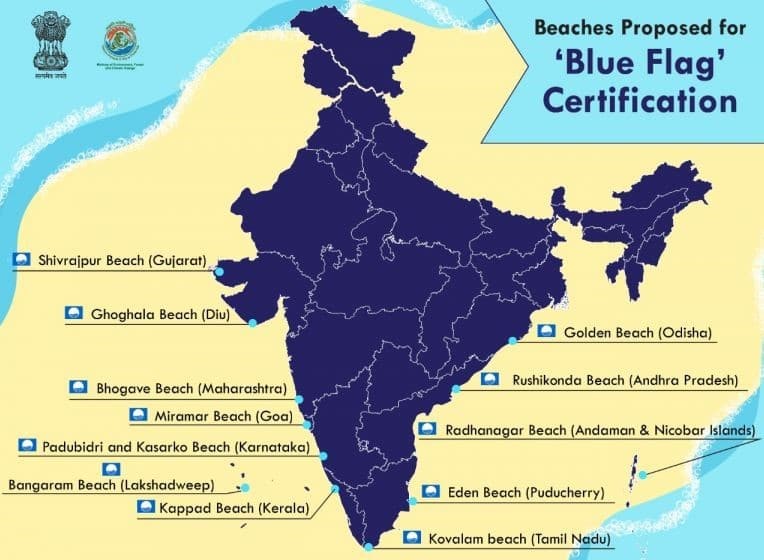
Blue flag beaches
Mission Circular Economy
Cheetah Reintroduction in India

|
Initiatives to promote circular bio economy |
|
References